本文主要对牛客网Verilog刷题中的企业真题进行记录。
根据RTL图编写Verilog程序
根据以下RTL图,使用 Verilog HDL语言编写代码,实现相同的功能,并编写testbench验证功能。
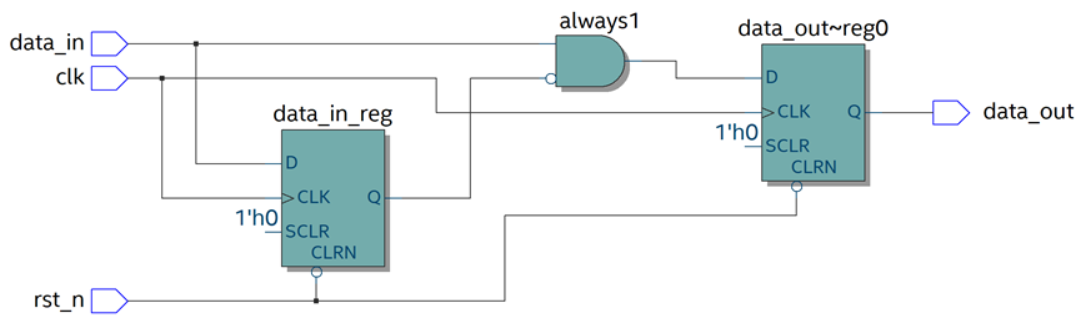
源代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30module RTL(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input data_in,
output reg data_out
);
reg data_in_reg;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
data_in_reg <= 1'b0;
end
else begin
data_in_reg <= data_in;
end
end
wire data_in_wire;
assign data_in_wire = data_in & ~data_in_reg;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
data_out <= 1'b0;
end
else begin
data_out <= data_in_wire;
end
end
endmodule
使用握手信号实现跨时钟域数据传输**
分别编写一个数据发送模块和一个数据接收模块,模块的时钟信号分别为clk_a,clk_b。两个时钟的频率不相同。数据发送模块循环发送0-15,在每个数据传输完成之后,间隔5个时钟,发送下一个数据。请在两个模块之间添加必要的握手信号,保证数据传输不丢失。模块的接口信号图如下:
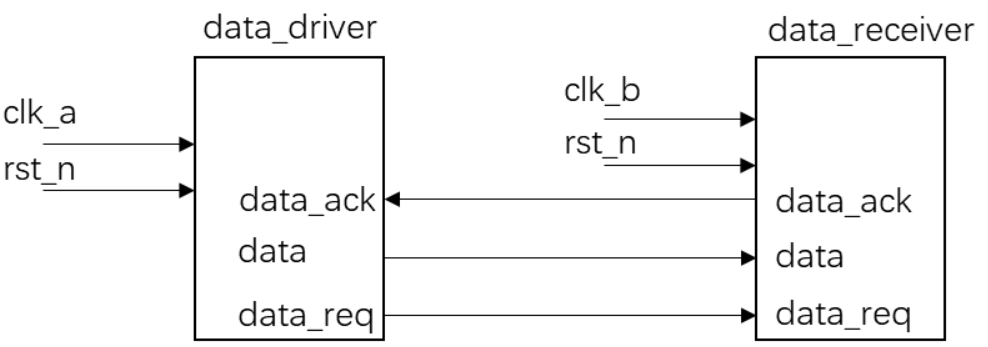
data_req和data_ack的作用说明:
- data_req表示数据请求接受信号。当data_out发出时,该信号拉高,在确认数据被成功接收之前,保持为高,期间data应该保持不变,等待接收端接收数据。
- 当数据接收端检测到data_req为高,表示该时刻的信号data有效,保存数据,并拉高data_ack。
- 当数据发送端检测到data_ack,表示上一个发送的数据已经被接收。撤销data_req,然后可以改变数据data。等到下次发送时,再一次拉高data_req。
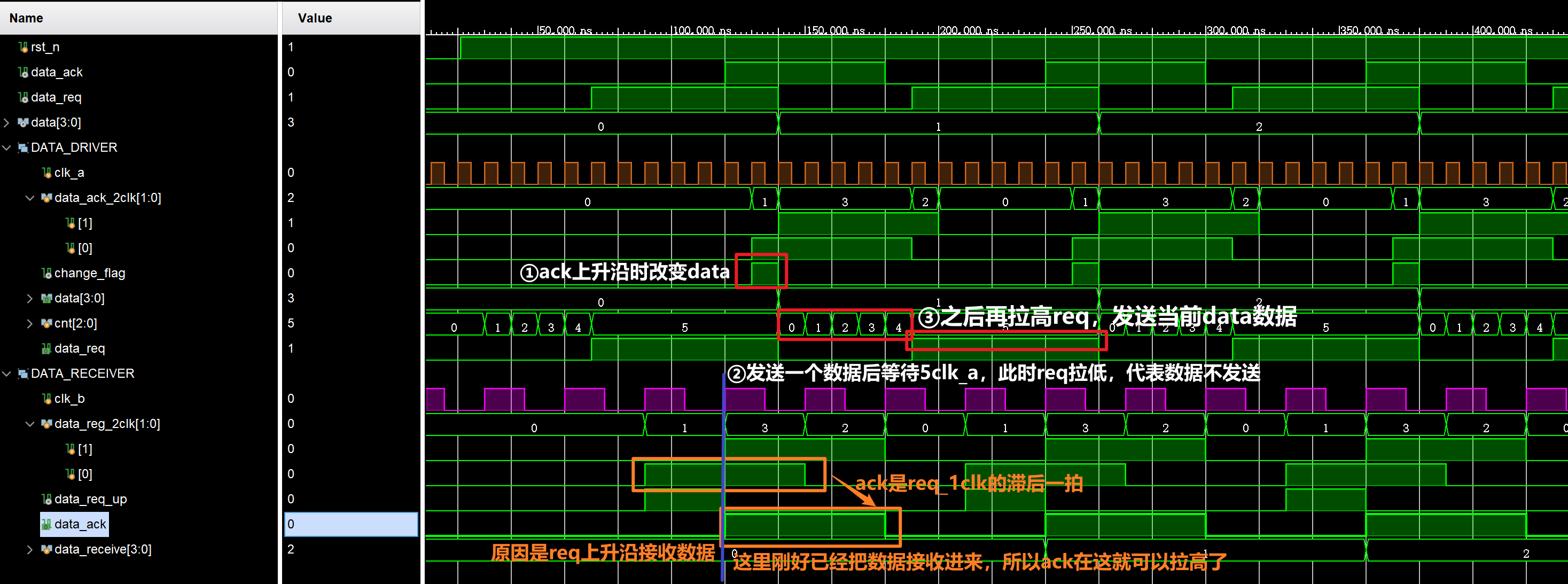
注意driver发送数据和receiver接收数据都是分别利用的ack与req的上升沿,时序结合仿真要细品
源代码:
data_driver.v
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73module data_driver(
input clk_a,
input rst_n,
input data_ack,
output reg [3:0]data,
output reg data_req
);
//data逻辑:data_ack上升沿作为data递增的标志
reg [1 : 0] data_ack_2clk;
wire change_flag;
always @(posedge clk_a or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
data_ack_2clk <= 'd0;
end
else begin
data_ack_2clk <= {data_ack_2clk[0], data_ack};
end
end
assign change_flag = ~data_ack_2clk[1] && data_ack_2clk[0];
always @(posedge clk_a or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
data <= 'd0;
end
else begin
if(change_flag) begin
data <= data + 1;
end
else begin
data <= data;
end
end
end
//在data_ack有效后,倒数5个时钟
reg [2 : 0] cnt;
always @(posedge clk_a or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
cnt <= 'd0;
end
else begin
if(change_flag) begin
cnt <= 'd0;
end
else if(data_req) begin
cnt <= cnt;
end
else begin
cnt <= cnt + 1;
end
end
end
//data_req逻辑
always @(posedge clk_a or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
data_req <= 1'b0;
end
else begin
if(cnt == 'd4) begin
data_req <= 1'b1;
end
else if(change_flag) begin
data_req <= 1'b0;
end
else begin
data_req <= data_req;
end
end
end
endmoduledata_receiver.v
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53module data_receiver(
input clk_b,
input rst_n,
input [3:0]data,
input data_req,
output reg data_ack
);
//将data_req打拍并判断上升沿
reg [1 : 0] data_reg_2clk;
wire data_req_up;
always @(posedge clk_b or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
data_reg_2clk <= 'd0;
end
else begin
data_reg_2clk <= {data_reg_2clk[0], data_req};
end
end
assign data_req_up = ~data_reg_2clk[1] && data_reg_2clk[0];
//提前1拍拉高data_ack
always @(posedge clk_b or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
data_ack <= 'd0;
end
else begin
if(data_reg_2clk[0]) begin
data_ack <= 'd1;
end
else begin
data_ack <= 'd0;
end
end
end
//上升沿时存储接收到的数据
reg [3 : 0] data_receive;
always @(posedge clk_b or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
data_receive <= 'd0;
end
else begin
if(data_req_up) begin
data_receive <= data;
end
else begin
data_receive <= data_receive;
end
end
end
endmodule
仿真结果:
自动售卖机**
请设计状态机电路,实现自动售卖机功能,A饮料5元钱,B饮料10元钱,售卖机可接收投币5元钱和10元钱,每次投币只可买一种饮料,考虑找零的情况。
电路的接口如下图所示。sel信号会先于din信号有效,且在购买一种饮料时值不变。
- sel为选择信号,用来选择购买饮料的种类,sel=0,表示购买A饮料,sel=1,表示购买B饮料;
- din表示投币输入,din=0表示未投币,din=1表示投币5元,din=2表示投币10元,不会出现din=3的情况;
- drinks_out表示饮料输出,drinks_out=0表示没有饮料输出,drinks_out=1表示输出A饮料,drinks_out=2表示输出B饮料,不出现drinks_out =3的情况,输出有效仅保持一个时钟周期;
- change_out表示找零输出,change_out=0表示没有找零,change_out=1表示找零5元,输出有效仅保持一个时钟周期。
我用摩尔型实现的,个人认为摩尔型比米粒型在实现这类逻辑时,虽然状态机更多,但输出逻辑更加简单,条理也会更清晰。而且要特别注意的是,该题要求的应该是对输入din的连续判断,与我在进阶题中刷到的自动售卖机不同(那题是只要出饮料就自动回到IDEL状态)
这里可以重点看看题解中替他人提供的代码(见reference),该代码中将sel和din合并之后再做次态判断,很妙,能有效减少ifelse的判断,从而减小组合逻辑的长度。
源代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110module sale (
input clk ,
input rst_n ,
input sel ,//sel=0,5$dranks,sel=1,10&=$drinks
input [1:0] din ,//din=1,input 5$,din=2,input 10$
output reg [1:0] drinks_out,//drinks_out=1,output 5$ drinks,drinks_out=2,output 10$ drinks
output reg change_out
);
//状态定义
localparam IDLE = 2'd0,
S_5Y = 2'd1,
S_10Y = 2'd2,
S_15Y = 2'd3;
//现态与次态定义
reg [1 : 0] cur_state, next_state;
//1.状态跳转
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
cur_state <= IDLE;
end
else begin
cur_state <= next_state;
end
end
//2.次态判断
always @(*) begin
next_state = cur_state;
case(cur_state)
IDLE: begin
case(din)
2'd0: next_state = IDLE;
2'd1: next_state = S_5Y;
2'd2: next_state = S_10Y;
default: next_state = IDLE;
endcase
end
S_5Y: begin
if(~sel) begin
case(din)
2'd0: next_state = IDLE;
2'd1: next_state = S_5Y;
2'd2: next_state = S_10Y;
default: next_state = IDLE;
endcase
end
else begin
case(din)
2'd0: next_state = S_5Y;
2'd1: next_state = S_10Y;
2'd2: next_state = S_15Y;
default: next_state = IDLE;
endcase
end
end
S_10Y: begin
case(din)
2'd0: next_state = IDLE;
2'd1: next_state = S_5Y;
2'd2: next_state = S_10Y;
default: next_state = IDLE;
endcase
end
S_15Y: begin
case(din)
2'd0: next_state = IDLE;
2'd1: next_state = S_5Y;
2'd2: next_state = S_10Y;
default: next_state = IDLE;
endcase
end
endcase
end
//3.结果输出
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
drinks_out <= 'd0;
end
else begin
case(next_state)
IDLE: drinks_out <= 'd0;
S_5Y: drinks_out <= sel ? 'd0 : 'd1;
S_10Y: drinks_out <= sel ? 'd2 : 'd1;
S_15Y: drinks_out <= 'd2;
default: drinks_out <= 'd0;
endcase
end
end
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
change_out <= 1'b0;
end
else begin
case(next_state)
IDLE: change_out <= 1'b0;
S_5Y: change_out <= 1'b0;
S_10Y: change_out <= sel ? 1'b0 : 1'b1;
S_15Y: change_out <= 1'b1;
default: change_out <= 1'b0;
endcase
end
end
endmodulereference:值得参考的代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
module sale(
input clk ,
input rst_n ,
input sel ,
input [1:0] din ,
output reg [1:0] drinks_out,
output reg change_out
);
parameter IDLE = 4'd0001;
parameter S_5 = 4'd0010;
parameter S_10 = 4'd0100;
parameter S_15 = 4'd1000;
reg [3:0] curr_state, next_state;
always @(posedge clk, negedge rst_n) begin
if (~rst_n) begin
curr_state <= IDLE;
next_state <= IDLE;
end
else begin
curr_state <= next_state;
end
end
wire [2:0] data_in;
assign data_in = {sel, din};
always @(*) begin
case (curr_state)
IDLE: begin
casex (data_in)
3'bx00: next_state = IDLE;
3'bx01: next_state = S_5;
3'bx10: next_state = S_10;
default: next_state = IDLE;
endcase
end
S_5: begin
casex (data_in)
3'b000: next_state = IDLE;
3'b001: next_state = S_5;
3'b010: next_state = S_10;
3'b100: next_state = S_5;
3'b101: next_state = S_10;
3'b110: next_state = S_15;
default: next_state = IDLE;
endcase
end
S_10: begin
casex (data_in)
3'bx00: next_state = IDLE;
3'bx01: next_state = S_5;
3'bx10: next_state = S_10;
default: next_state = IDLE;
endcase
end
S_15: begin
casex (data_in)
3'b100: next_state = IDLE;
3'b101: next_state = S_5;
3'b110: next_state = S_10;
default: next_state = IDLE;
endcase
end
endcase
end
always @(posedge clk, negedge rst_n) begin
case (next_state)
S_5: begin
drinks_out <= (sel) ? 'd0 : 'd1;
change_out <= 'd0;
end
S_10: begin
drinks_out <= (sel) ? 'd2 : 'd1;
change_out <= (sel) ? 'd0 : 'd1;
end
S_15: begin
drinks_out <= 'd2;
change_out <= 'd1;
end
default: begin
drinks_out <= 'd0;
change_out <= 'd0;
end
endcase
end
endmodule
序列发生器
编写一个模块,实现循环输出序列001011。
源代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27module sequence_generator(
input clk,
input rst_n,
output reg data
);
reg [5 : 0] q; //001011
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
q <= 6'b001011;
end
else begin
q <= {q[4 : 0], q[5]};
end
end
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
data <= 1'b0;
end
else begin
data <= q[5];
end
end
endmodule
并串转换*
设计一个模块进行并串转换,要求每四位d输入转到一位dout输出,输出valid_in表示此时的输入有效
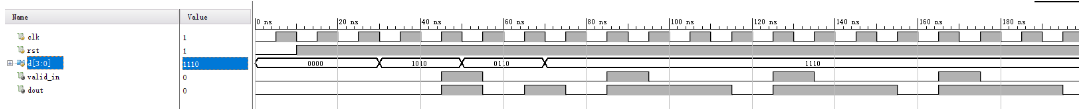
这里有个很巧妙的地方是,利用cnt去判断左移,做的时候没想到,卡了很久,一直在想如何实现先最高位,然后每个clk再左移
源代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55module huawei5(
input wire clk ,
input wire rst ,
input wire [3:0]d ,
output wire valid_in ,
output wire dout
);
//valid信号相关计数器,复位后,每4clk,valid_in就拉高1clk
reg [1 : 0] Cnt_valid;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst) begin
if(~rst) begin
Cnt_valid <= 'd0;
end
else begin
Cnt_valid <= Cnt_valid + 1;
end
end
//valid_in逻辑
reg valid_in_r;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst) begin
if(~rst) begin
valid_in_r <= 'd0;
end
else begin
if(Cnt_valid == 3) begin
valid_in_r <= 'd1;
end
else begin
valid_in_r <= 'd0;
end
end
end
assign valid_in = valid_in_r;
//当valid_in有效时,保存输入的数据并左移
reg [3 : 0] d_r;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst) begin
if(~rst) begin
d_r <= 'd0;
end
else begin
if(Cnt_valid == 3) begin
d_r <= d;
end
else begin
d_r <= d_r << 1;
end
end
end
assign dout = d_r[3];
endmodule
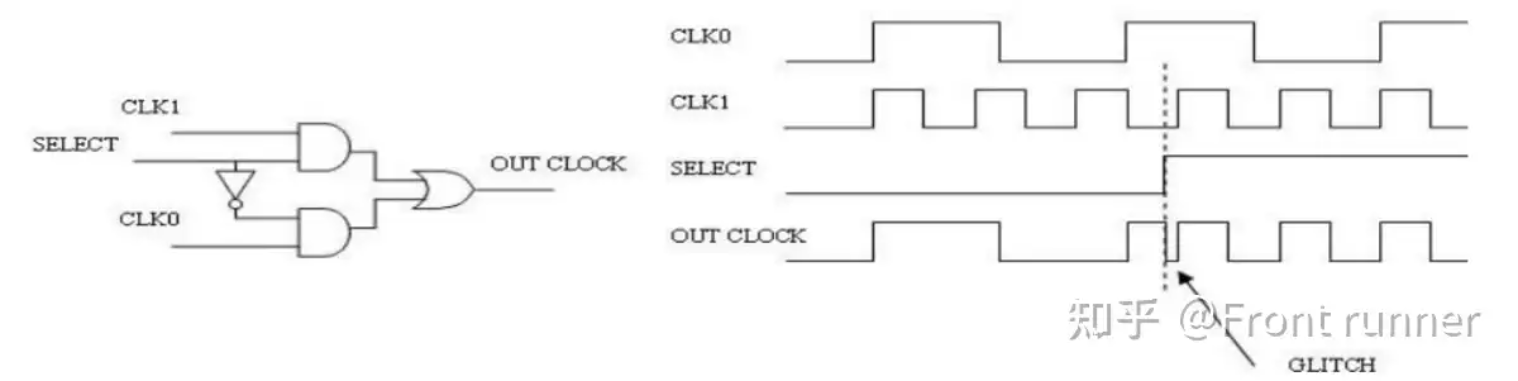
时钟切换*
存在两个同步的倍频时钟clk0 clk1,已知clk0是clk1的二倍频,现在要设计一个切换电路,sel选择时候进行切换,要求没有毛刺。
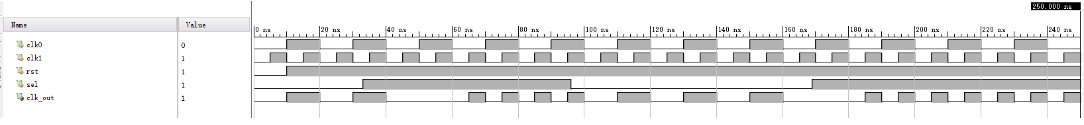
首先需要意识到:一个时钟源转换到另一个时钟源时容易产生毛刺
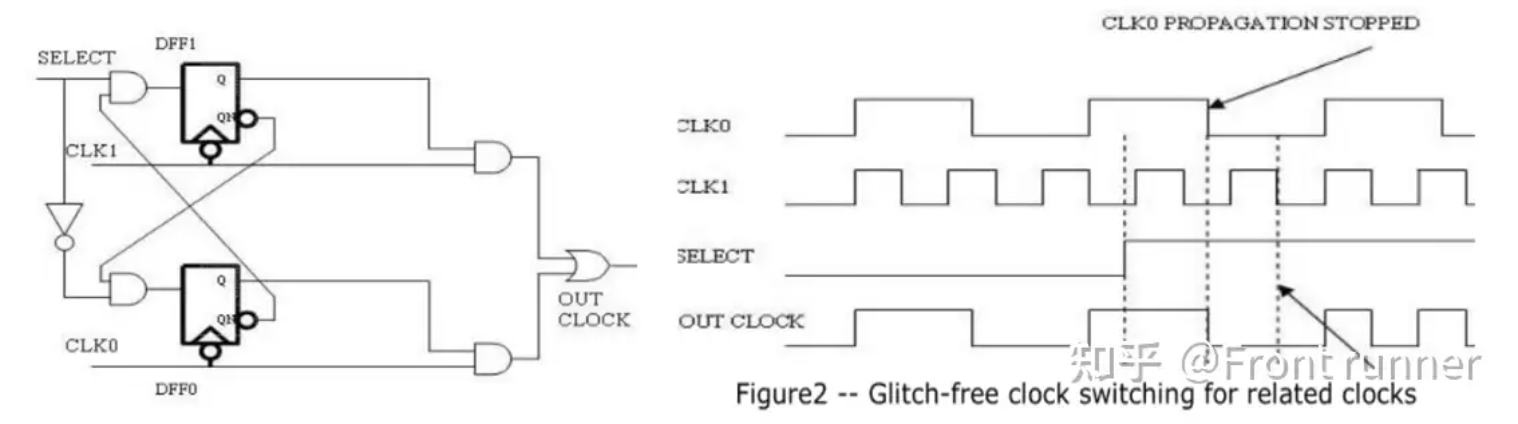
解决方法是:在sel判断之间加一个双下降沿触发器(reference中还有非相关时钟的解决办法,即在下降沿触发器前再加一个上升沿触发器)
源代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27module huawei6(
input wire clk0 ,
input wire clk1 ,
input wire rst ,
input wire sel ,
output reg clk_out
);
reg q0, q1;
always@(negedge clk0 or negedge rst)
if(!rst)
q0 <= 0;
else
q0 <= ~sel & ~q1;
always@(negedge clk1 or negedge rst)
if(!rst)
q1 <= 0;
else
q1 <= sel & ~q0;
always @(*) begin
clk_out = (q0 & clk0) | (q1 & clk1);
end
endmodulereference:
状态机与时钟分频
使用状态机实现时钟分频,要求对时钟进行四分频,占空比为0.25

其实就是用状态机实现了4点计数
源代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48module huawei7(
input wire clk ,
input wire rst ,
output reg clk_out
);
//状态机
localparam S_1 = 2'd0,
S_2 = 2'd1,
S_3 = 2'd2,
S_4 = 2'd3;
reg [1 : 0] cur_state, next_state;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst) begin
if(~rst) begin
cur_state <= S_1;
end
else begin
cur_state <= next_state;
end
end
always @(*) begin
next_state = cur_state;
case(cur_state)
S_1: next_state = S_2;
S_2: next_state = S_3;
S_3: next_state = S_4;
S_4: next_state = S_1;
endcase
end
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst) begin
if(~rst) begin
clk_out <= 'd0;
end
else begin
if(next_state == S_2) begin
clk_out <= 'd1;
end
else begin
clk_out <= 'd0;
end
end
end
endmodule
超前进位加法器**
求两个四位的数据编写一个四位的超前进位加法器
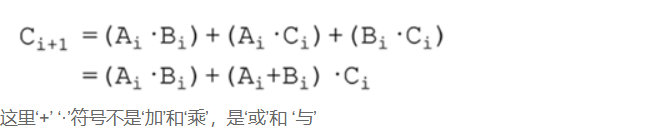
原理可参考我的另一篇博客里的超前进位加法器:FPGA数字信号处理之加法器与乘法器的设计 | ssy的小天地 (ssy1938010014.github.io),但它的推导公式与题目中的有一点点不一样,但最终结果是一样的,因为(a&b)|(c&(a^b))和(a&b)|(a|b)&c是等价的,下面这个图还挺形象的
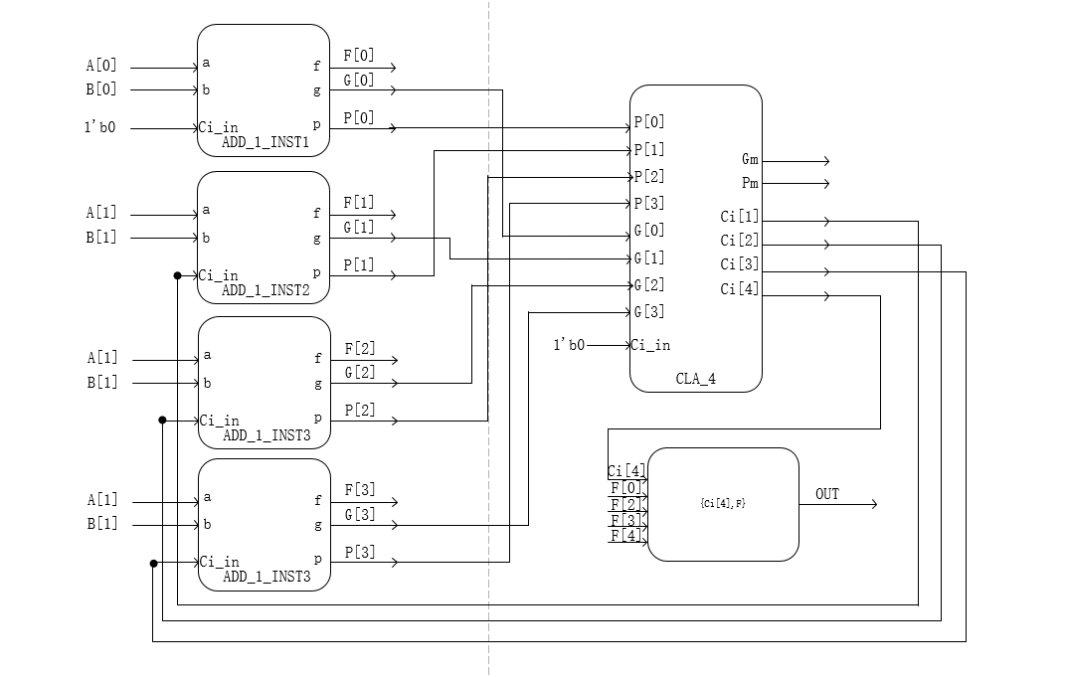
源代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56module huawei8//四位超前进位加法器
(
input wire [3:0]A,
input wire [3:0]B,
output wire [4:0]OUT
);
wire [3:0] P;
wire [3:0] G;
wire [3:0] F;
wire [4:1] C;
//*************code***********//
CLA_4 cla_inst(.P(P),.G(G),.C_in(1'b0),.Ci(C),.Gm(),.Pm());
Add1 a1(.a(A[0]), .b(B[0]), .C_in(1'b0), .f(F[0]), .g(G[0]), .p(P[0]));
Add1 a2(.a(A[1]), .b(B[1]), .C_in(C[1]), .f(F[1]), .g(G[1]), .p(P[1]));
Add1 a3(.a(A[2]), .b(B[2]), .C_in(C[2]), .f(F[2]), .g(G[2]), .p(P[2]));
Add1 a4(.a(A[3]), .b(B[3]), .C_in(C[3]), .f(F[3]), .g(G[3]), .p(P[3]));
assign OUT = {C[4],F};
//*************code***********//
endmodule
//////////////下面是两个子模块////////
module Add1
(
input a,
input b,
input C_in,
output f,
output g,
output p
);
assign g = a | b;
assign f = a ^ b ^ C_in;
assign p = a & b;
endmodule
module CLA_4(
input [3:0]P,
input [3:0]G,
input C_in,
output [4:1]Ci,
output Gm,
output Pm
);
assign Ci[1] = P[0] | G[0];
assign Ci[2] = P[1] | G[1] & Ci[1];
assign Ci[3] = P[2] | G[2] & Ci[2];
assign Ci[4] = P[3] | G[3] & Ci[3];
endmodule
十六进制计数器
请用Verilog设计十六进制递增计数器电路,每个时钟周期递增1。
源代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17module counter_16(
input clk ,
input rst_n ,
output reg [3:0] Q
);
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
Q <= 'd0;
end
else begin
Q <= Q + 1;
end
end
endmodule
同步FIFO
请设计带有空满信号的同步FIFO,FIFO的深度和宽度可配置。双口RAM的参考代码和接口信号已给出,请在答案中添加并例化此部分代码。
源代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124/**********************************RAM************************************/
module dual_port_RAM #(parameter DEPTH = 16,
parameter WIDTH = 8)(
input wclk
,input wenc
,input [$clog2(DEPTH)-1:0] waddr
,input [WIDTH-1:0] wdata
,input rclk
,input renc
,input [$clog2(DEPTH)-1:0] raddr
,output reg [WIDTH-1:0] rdata
);
reg [WIDTH-1:0] RAM_MEM [0:DEPTH-1];
always @(posedge wclk) begin
if(wenc)
RAM_MEM[waddr] <= wdata;
end
always @(posedge rclk) begin
if(renc)
rdata <= RAM_MEM[raddr];
end
endmodule
/**********************************SFIFO************************************/
module sfifo#(
parameter WIDTH = 8,
parameter DEPTH = 16
)(
input clk ,
input rst_n ,
input winc ,
input rinc ,
input [WIDTH-1:0] wdata ,
output reg wfull ,
output reg rempty ,
output wire [WIDTH-1:0] rdata
);
//空满标志
wire fifo_full, fifo_empty;
//读写指针
reg [$clog2(DEPTH) : 0] read_point, write_point;
//RAM例化
dual_port_RAM #(
.EPTH(DEPTH),
.IDTH(WIDTH)
)dual_port_RAM_U1(
.wclk (clk),
.wenc (winc && ~fifo_full),
.waddr (write_point[$clog2(DEPTH) - 1 : 0]),
.wdata (wdata),
.rclk (clk),
.renc (rinc && ~fifo_empty),
.raddr (read_point[$clog2(DEPTH) - 1 : 0]),
.rdata (rdata)
);
//读写指针逻辑
//写指针
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
write_point <= 'd0;
end
else begin
if(winc && ~fifo_full) begin
write_point <= write_point + 1;
end
end
end
//读指针
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
read_point <= 'd0;
end
else begin
if(rinc && ~fifo_empty) begin
read_point <= read_point + 1;
end
end
end
//空满标志判断逻辑
assign fifo_empty = read_point == write_point;
assign fifo_full = read_point == {~write_point[$clog2(DEPTH)], write_point[$clog2(DEPTH) - 1 : 0]};
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
wfull <= 'd0;
end
else begin
if(fifo_full) begin
wfull <= 'd1;
end
else begin
wfull <= 'd0;
end
end
end
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
rempty <= 'd0;
end
else begin
if(fifo_empty) begin
rempty <= 'd1;
end
else begin
rempty <= 'd0;
end
end
end
endmodule
脉冲同步器(快到慢)
sig_a 是 clka(300M)时钟域的一个单时钟脉冲信号(高电平持续一个时钟clka周期),请设计脉冲同步电路,将sig_a信号同步到时钟域 clkb(100M)中,产生sig_b单时钟脉冲信号(高电平持续一个时钟clkb周期)输出。请用 Verilog 代码描述。clka时钟域脉冲之间的间隔很大,无需考虑脉冲间隔太小的问题。
源代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46module pulse_detect(
input clka ,
input clkb ,
input rst_n ,
input sig_a ,
output sig_b
);
//在快时钟域将脉冲信号转化为电平信号
reg level_in_fastclk;
always @(posedge clka or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
level_in_fastclk <= 'd0;
end
else begin
level_in_fastclk <= sig_a ? ~level_in_fastclk : level_in_fastclk;
end
end
//跨时钟域打两拍处理,在慢时钟域下
wire SyncLevel_in_slowclk;
reg [1 : 0] SyncLevel_in_slowclk_r;
always @(posedge clkb or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
SyncLevel_in_slowclk_r <= 'd0;
end
else begin
SyncLevel_in_slowclk_r <= {SyncLevel_in_slowclk_r[0], level_in_fastclk};
end
end
assign SyncLevel_in_slowclk = SyncLevel_in_slowclk_r[1];
//在慢时钟域将电平信号转化为脉冲信号(即边沿检测)
reg SyncLevel_in_slowclk_1clk;
always @(posedge clkb or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
SyncLevel_in_slowclk_1clk <= 'd0;
end
else begin
SyncLevel_in_slowclk_1clk <= SyncLevel_in_slowclk;
end
end
assign sig_b = SyncLevel_in_slowclk_1clk ^ SyncLevel_in_slowclk;
endmodule
序列检测器(Moore型)
请用Moore型状态机实现序列“1101”从左至右的不重叠检测。电路的接口如下图所示。当检测到“1101”,Y输出一个时钟周期的高电平脉冲。
源代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51module det_moore(
input clk ,
input rst_n ,
input din ,
output reg Y
);
localparam IDLE = 3'd0,
S0 = 3'd1,
S1 = 3'd2,
S2 = 3'd3,
S3 = 3'd4;
reg [2 : 0] cur_state, next_state;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
cur_state <= IDLE;
end
else begin
cur_state <= next_state;
end
end
always @(*) begin
next_state = cur_state;
case(cur_state)
IDLE: next_state = din ? S0 : IDLE;
S0: next_state = din ? S1 : IDLE;
S1: next_state = din ? IDLE : S2;
S2: next_state = din ? S3 : IDLE;
S3: next_state = IDLE;
endcase
end
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
Y <= 'd0;
end
else begin
if(cur_state == S3) begin
Y <= 'd1;
end
else begin
Y <= 'd0;
end
end
end
endmodule
乘法与位运算*
进行一个运算单元的电路设计,A[7:0]*11111011,尽量用最少的资源实现,写出对应的 RTL 代码。
观察乘数的特点: 1111_1011 = 1_0000_0000 - 1 - 100;因为1_0000_0000 - 1 = 1111_1111,再减去100,故为题目中的乘数。(主要是凑成$2^N$次形式用移位运算实现)
源代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8module dajiang13(
input [7:0] A,
output [15:0] B
);
assign B = (A << 8) - A - (A << 2);
endmodule
全加器*
- 请用题目提供的半加器实现全加器电路
思路:
- ①先将A和B用半加器加起来,生成和是s[0]和进位信号c[0];
- ②然后第一个半加器生成的和s[0]与Ci用半加器相加,得到的和s[1]即为全加器的和S;
- ③全加器进位信号的生成是这样:两次半加器产生的进位信号有一个为1,则全加器的进位信号Co为1。
源代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44module add_half(
input A ,
input B ,
output wire S ,
output wire C
);
assign S = A ^ B;
assign C = A & B;
endmodule
/***************************************************************/
module add_full(
input A ,
input B ,
input Ci ,
output wire S ,
output wire Co
);
wire sum_A_B;
wire Carry_A_B;
wire s2,c2;
add_half add_half_U1 (
.A(A),
.B(B),
.S(sum_A_B),
.C(Carry_A_B)
);
add_half add_half_U2 (
.A(sum_A_B),
.B(Ci),
.S(s2),
.C(c2)
);
assign S = s2;
assign Co = Carry_A_B | c2;
endmodule
串行进位加法器
请用全加器电路实现串行进位的4位全加器电路
源代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92module add_4(
input [3:0] A ,
input [3:0] B ,
input Ci ,
output wire [3:0] S ,
output wire Co
);
wire [3 : 0] Co_w;
add_full add_full_u1(
.A (A[0]),
.B (B[0]),
.Ci (Ci),
.S (S[0]),
.Co (Co_w[0])
);
add_full add_full_u2(
.A (A[1]),
.B (B[1]),
.Ci (Co_w[0]),
.S (S[1]),
.Co (Co_w[1])
);
add_full add_full_u3(
.A (A[2]),
.B (B[2]),
.Ci (Co_w[1]),
.S (S[2]),
.Co (Co_w[2])
);
add_full add_full_u4(
.A (A[3]),
.B (B[3]),
.Ci (Co_w[2]),
.S (S[3]),
.Co (Co_w[3])
);
assign Co = Co_w[3];
endmodule
module add_half(
input A ,
input B ,
output wire S ,
output wire C
);
assign S = A ^ B;
assign C = A & B;
endmodule
/***************************************************************/
module add_full(
input A ,
input B ,
input Ci ,
output wire S ,
output wire Co
);
wire c_1;
wire c_2;
wire sum_1;
add_half add_half_1(
.A (A),
.B (B),
.S (sum_1),
.C (c_1)
);
add_half add_half_2(
.A (sum_1),
.B (Ci),
.S (S),
.C (c_2)
);
assign Co = c_1 | c_2;
endmodule
异步复位同步释放*
请使用异步复位同步释放来将输入数据d存储到寄存器中,并画图说明异步复位同步释放的机制原理。
既解决了同步复位的资源消耗问题,又解决了异步复位的亚稳态问题,其根本思想是异步信号同步化
同步复位:
优点:
- 抗干扰性高,可以剔除复位信号中周期短于时钟周期的毛刺
- 电路稳定性强
缺点:
- 大多数逻辑器件的目标库内的DFF都只有异步复位端口,适用同步复位时,综合器就会在寄存器的数据输入端插入组合逻辑,占用更多的逻辑资源
- 同步复位依赖于时钟,如果电路中的时钟信号出现问题,无法完成复位
- 对复位信号的脉冲宽度有要求,必须大于指定的时钟周期,由于线路上的延迟,可能需要多个时钟周期的复位脉冲宽度,且很难保证复位信号到达各个寄存器的时序
异步复位:
优点:
- 复位信号不是数据路径的一部分,不是触发器D输入的一部分
- 异步复位信号识别方便,而且可以很方便的使用全局复位
- 由于大多数的厂商目标库内的触发器都有异步复位端口,可以节约逻辑资源
缺点:
复位信号容易受到毛刺的影响
复位信号释放的随机性,可能导致时序违规,倘若复位释放时恰恰在时钟有效沿附近,就很容易使电路处于亚稳态
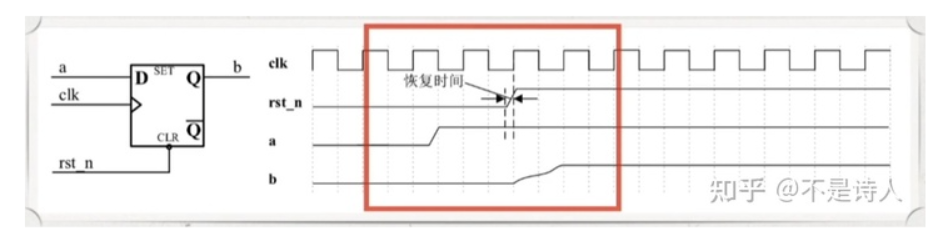
源代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31module ali16(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input d,
output reg dout
);
reg rst_0;
reg rst_1;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
rst_0 <= 1'b0;
rst_1 <= 1'b0; //异步复位
end
else begin
rst_0 <= 1'b1;
rst_1 <= rst_0;
end
end
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_1) begin
if(~rst_1) begin
dout <= 'd0;
end
else begin
dout <= d;
end
end
endmodule
求最小公倍数**
设计一个时序电路,输入2个无符号数,位宽可以通过参数DATA_W确定,输出这两个数的最小公倍数和最大公约数。
对于最小公倍数和最大公约数的求解,一般使用辗转相除法/更相减损法计算得到最大公约数,再利用两数的乘积除以最大公约数得到最小公倍数
详细设计思路可参考:【Verilog学习日常】—牛客网刷题—Verilog企业真题—VL75_最小公倍数和最大公约数verilog-CSDN博客。网上的二段式状态机设计仿真结果:
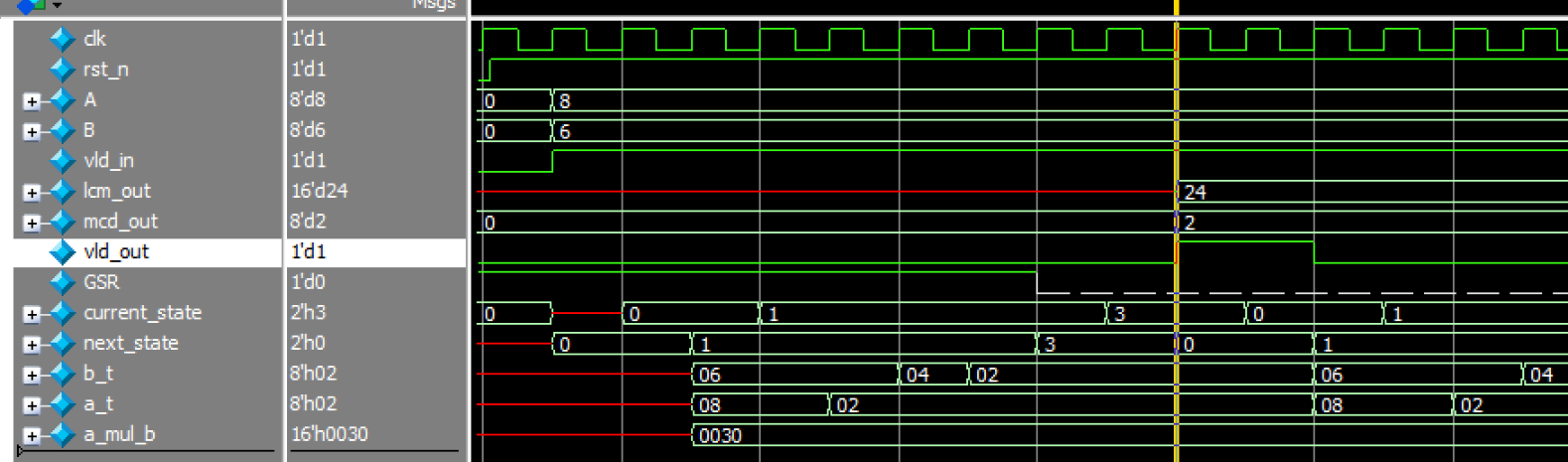
源代码:(这是我的三段式状态机的设计思路,根据仿真结果显示是没有问题的,但过不了牛客网的测试,应该是牛客网设定的答案时序与我差了几个clk)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115module lcm#(
parameter DATA_W = 8)
(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input [DATA_W - 1 : 0] A,
input [DATA_W - 1 : 0] B,
input vld_in,
output wire [DATA_W * 2 - 1 : 0] lcm_out,
output wire [DATA_W - 1 : 0] mcd_out,
output reg vld_out
);
//状态定义
localparam IDLE = 2'd0,
S1 = 2'd1,
S2 = 2'd2;
//次态与现态
reg [1 : 0] cur_state, next_state;
//次态判断相关变量
reg [DATA_W - 1 : 0] a_t, b_t;
reg [DATA_W - 1 : 0] mcd_out_r;
reg [DATA_W * 2 - 1 : 0] multi_AB;
//1.状态跳转
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
cur_state <= IDLE;
end
else begin
cur_state <= next_state;
end
end
//2.状态跳转
always @(*) begin
next_state = cur_state;
case(cur_state)
IDLE: next_state = vld_in ? S1 : IDLE;
S1: next_state = (a_t == b_t) ? S2 : S1;
S2: next_state = IDLE;
default: next_state = IDLE;
endcase
end
//3.输出判断
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
vld_out <= 'd0;
end
else begin
if(next_state == S2) begin
vld_out <= 'd1;
end
else begin
vld_out <= 'd0;
end
end
end
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
mcd_out_r <= 'd0;
end
else begin
if(next_state == S2) begin
mcd_out_r <= a_t;
end
end
end
assign mcd_out = mcd_out_r;
assign lcm_out = multi_AB / mcd_out;
//更相减损法
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
a_t <= 'd0;
b_t <= 'd0;
multi_AB <= 'd0; //这里把multi_AB放这写只有为了求最小公倍数,懒得单独开个always写了
end
else begin
case(cur_state)
IDLE: begin
if(vld_in) begin
a_t <= A;
b_t <= B;
multi_AB <= A * B;
end
end
S1: begin
if(a_t > b_t) begin
a_t <= a_t - b_t;
b_t <= b_t;
end
else if(a_t < b_t) begin
b_t <= b_t - a_t;
a_t <= a_t;
end
end
S2: begin
a_t <= a_t;
b_t <= b_t;
end
default: begin
a_t <= 'd0;
b_t <= 'd0;
end
endcase
end
end
endmodule仿真结果:
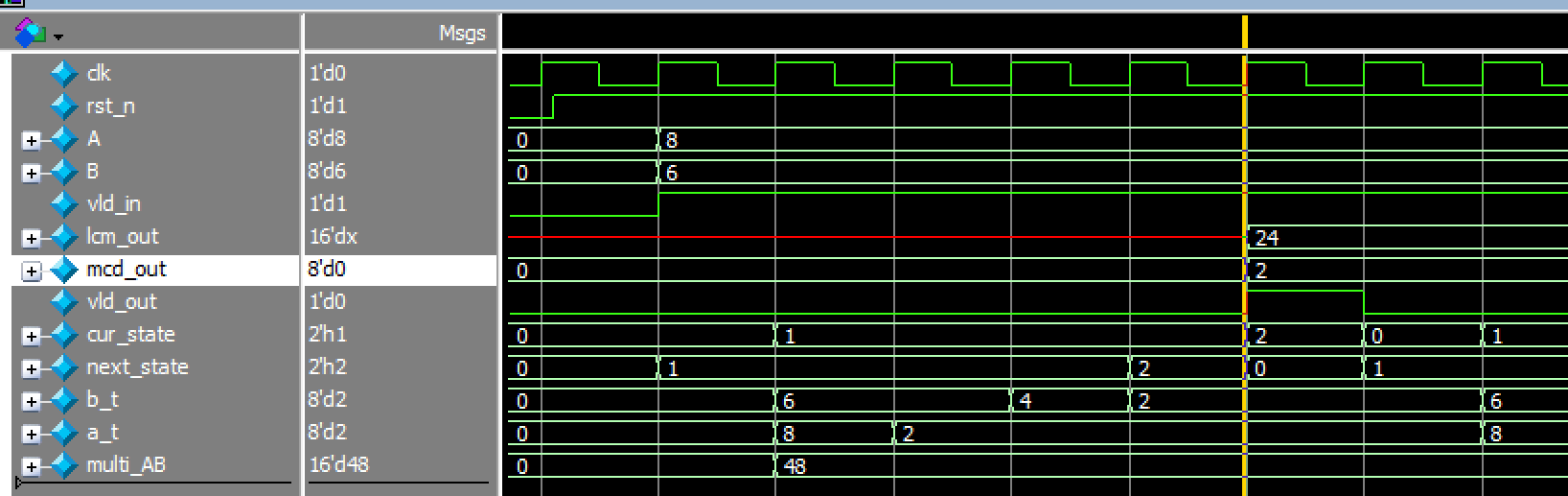
任意奇数倍时钟分频**
编写一个模块,对输入的时钟信号clk_in,实现任意奇数分频,要求分频之后的时钟信号占空比为50%。模块应包含一个参数,用于指定分频的倍数。
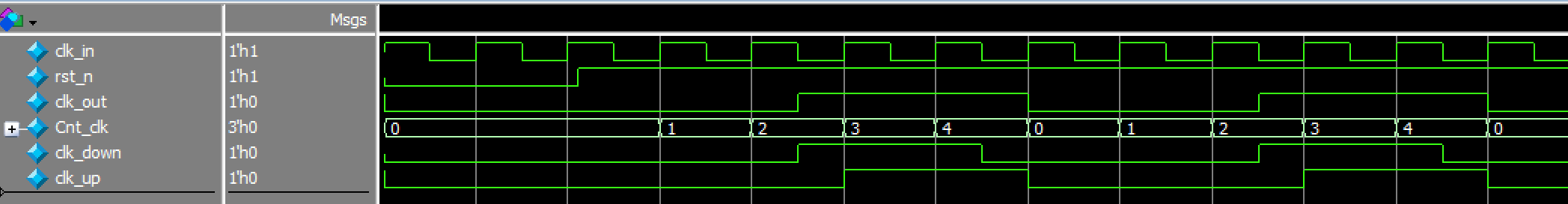
这里需要注意的是复位后,分频时钟是先低后高还是先高后低
先高后低仿真结果
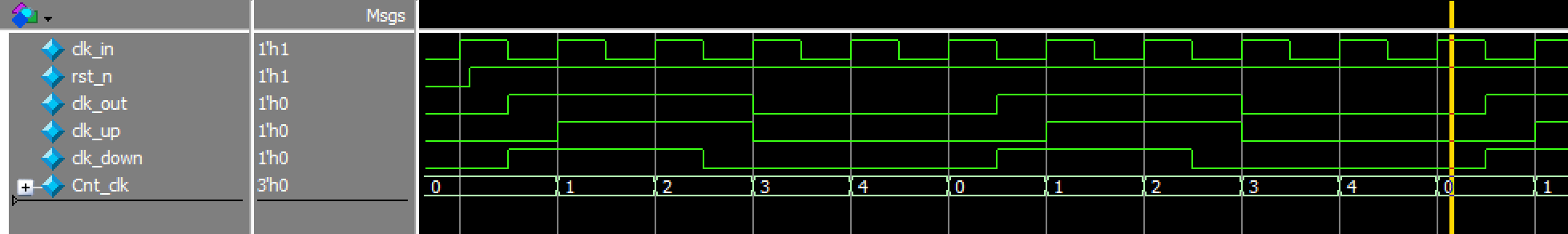
先低后高仿真结果
源代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103module clk_divider #(
parameter dividor = 5
)(
input clk_in,
input rst_n,
output clk_out
);
//##############复位后先高后低写法
// reg [$clog2(dividor) - 1 : 0] Cnt_clk;
// always @(posedge clk_in or negedge rst_n) begin
// if(~rst_n) begin
// Cnt_clk <= 'd0;
// end
// else begin
// if(Cnt_clk == dividor - 1) begin
// Cnt_clk <= 'd0;
// end
// else begin
// Cnt_clk <= Cnt_clk + 1;
// end
// end
// end
// reg clk_up;
// reg clk_down;
// always @(posedge clk_in or negedge rst_n) begin
// if(~rst_n) begin
// clk_up <= 'd0;
// end
// else begin
// if(Cnt_clk < (dividor - 1) / 2) begin
// clk_up <= 'd1;
// end
// else begin
// clk_up <= 'd0;
// end
// end
// end
// always @(negedge clk_in or negedge rst_n) begin
// if(~rst_n) begin
// clk_down <= 'd0;
// end
// else begin
// if(Cnt_clk < (dividor - 1) / 2) begin
// clk_down <= 'd1;
// end
// else begin
// clk_down <= 'd0;
// end
// end
// end
// assign clk_out = clk_up | clk_down;
//#################复位后先高后低写法
reg [$clog2(dividor) - 1 : 0] Cnt_clk;
always @(posedge clk_in or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
Cnt_clk <= 'd0;
end
else begin
if(Cnt_clk == dividor - 1) begin
Cnt_clk <= 'd0;
end
else begin
Cnt_clk <= Cnt_clk + 1;
end
end
end
reg clk_up;
reg clk_down;
always @(posedge clk_in or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
clk_up <= 'd0;
end
else begin
if(Cnt_clk < (dividor - 1) / 2 || (Cnt_clk == dividor - 1)) begin
clk_up <= 'd0;
end
else begin
clk_up <= 'd1;
end
end
end
always @(negedge clk_in or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
clk_down <= 'd0;
end
else begin
if(Cnt_clk < (dividor - 1) / 2 || (Cnt_clk == dividor - 1)) begin
clk_down <= 'd0;
end
else begin
clk_down <= 'd1;
end
end
end
assign clk_out = clk_up | clk_down;
endmodule
编写乘法器求解算法表达式*
编写一个4bit乘法器模块,并例化该乘法器求解c=12a+5b,其中输入信号a,b为4bit无符号数,c为输出。注意请不要直接使用*符号实现乘法功能。
严重怀疑牛客网的编译器有问题,下面这段代码如果mul_a与mul_b交换位置的话,结果就会提前1clk出来,然后测试就不通过了。不过下面这段generate拆分乘法的方式可以记录一下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7//组合逻辑分解乘法->加法
genvar i;
generate
for(i = 0; i < 4; i = i + 1) begin
assign temp[i] = mul_a[i] ? {{(4 - i){1'b0}}, mul_b, {i{1'b0}}} : 'd0;
end
endgenerate源代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63module calculation(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input [3:0] a,
input [3:0] b,
output [8:0] c
);
wire [7 : 0] mul_out_1, mul_out_2;
multi multi_U1(
.clk (clk ),
.rst_n (rst_n ),
.mul_a (a ),
.mul_b (4'd12 ),
.mul_out (mul_out_1)
);
multi multi_U2(
.clk (clk ),
.rst_n (rst_n ),
.mul_a (b ),
.mul_b (4'd5 ),
.mul_out (mul_out_2)
);
assign c = mul_out_1 + mul_out_2;
endmodule
module multi#(
parameter size = 4
)(
input clk ,
input rst_n ,
input [size-1:0] mul_a ,
input [size-1:0] mul_b ,
output reg [size*2-1:0] mul_out
);
//中间结果暂存
wire [size * 2 - 1 : 0] temp[3 : 0];
//组合逻辑分解乘法->加法
genvar i;
generate
for(i = 0; i < 4; i = i + 1) begin
assign temp[i] = mul_a[i] ? {{(4 - i){1'b0}}, mul_b, {i{1'b0}}} : 'd0;
end
endgenerate
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n) begin
mul_out <= 'd0;
end
else begin
mul_out <= temp[0] + temp[1] + temp[2] + temp[3];
end
end
endmodule
