C++之内存模型与名称空间……
多文件编译
头文件中常包含的内容:
- 使用#define或const定义的符号常量
- 函数原型
- 结构声明
- 类声明
- 模板声明
- 内联函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
struct polar
{
double distance;
double angle;
};
struct rect
{
double x;
double y;
};
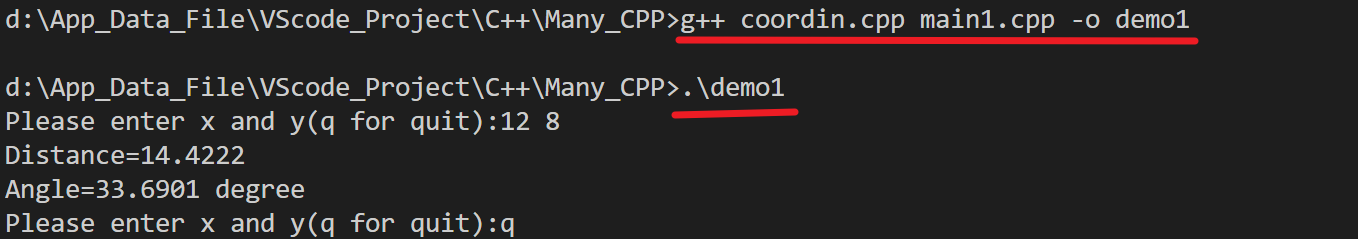
polar rect_to_polar(rect xypos);
void show_polar(polar pplace);VScode中如何对多个CPP文件进行编译
1
2g++ 文件名1.cpp 文件名2.cpp -o 重命名
.\重命名CPP文件:
- coordin.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
using namespace std;
polar rect_to_polar(rect xypos)
{
polar pplace;
pplace.distance=sqrt(xypos.x*xypos.x+xypos.y*xypos.y);
pplace.angle=atan2(xypos.y,xypos.x);//返回的是弧度制
return pplace;
}
void show_polar(polar pplace)
{
const double Rad_to_deg=57.29577951;
cout<<"Distance="<<pplace.distance<<endl;
//将弧度制转化为角度制
cout<<"Angle="<<pplace.angle*Rad_to_deg<<" degree"<<endl;
}- main1.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
rect rplace;
polar pplace;
cout<<"Please enter x and y(q for quit):";
while(cin>>rplace.x>>rplace.y)
{
pplace=rect_to_polar(rplace);
show_polar(pplace);
cout<<"Please enter x and y(q for quit):";
}
return 0;
}
Extern与::的使用
extern访问别的源文件中的全局变量,通常在头文件中声明::强制访问全局变量,而不访问离得最近的局部变量头文件:support.h
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
extern double warming;
void update(double dt);
void local(void);源文件:
- support.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
using namespace std;
void update(double dt)
{
warming+=dt;
cout<<"Updating global warming to "<<warming<<" degrees"<<endl;
}
void local(void)
{
double warming=0.8;
cout<<"Local warming="<<warming<<" degrees"<<endl;
cout<<"Global warming in Local ="<<::warming<<" degrees"<<endl;
}- main.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
using namespace std;
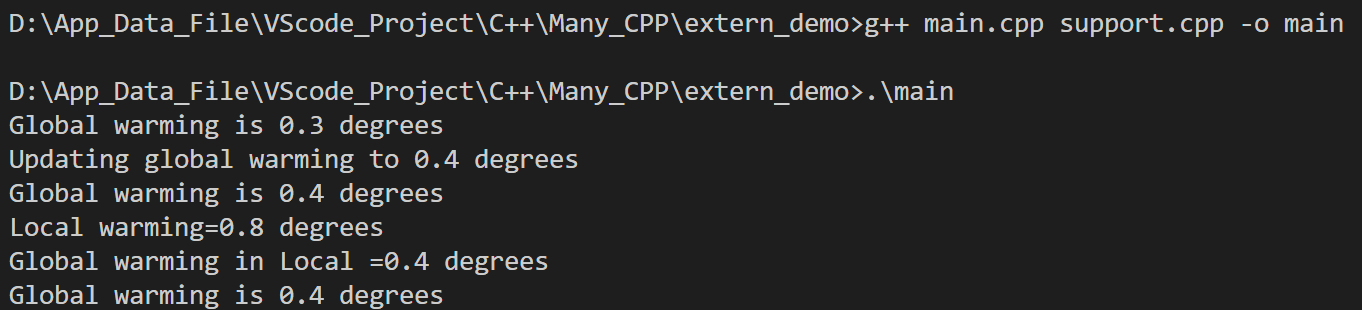
double warming=0.3;
int main(void)
{
cout<<"Global warming is "<<warming<<" degrees"<<endl;
update(0.1);
cout<<"Global warming is "<<warming<<" degrees"<<endl;
local();
cout<<"Global warming is "<<warming<<" degrees"<<endl;
return 0;
}结果如下:
Static的使用
当对全局变量使用Static时,表示此全局变量只用于当前文件,不能被其他文件访问
在函数中使用Static时:只初始化一次,且在函数调用完后变量不会消失
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
using namespace std;
const int ArSize=10;
void strcount(const char *str);
int main(void)
{
char input[ArSize];
char next;
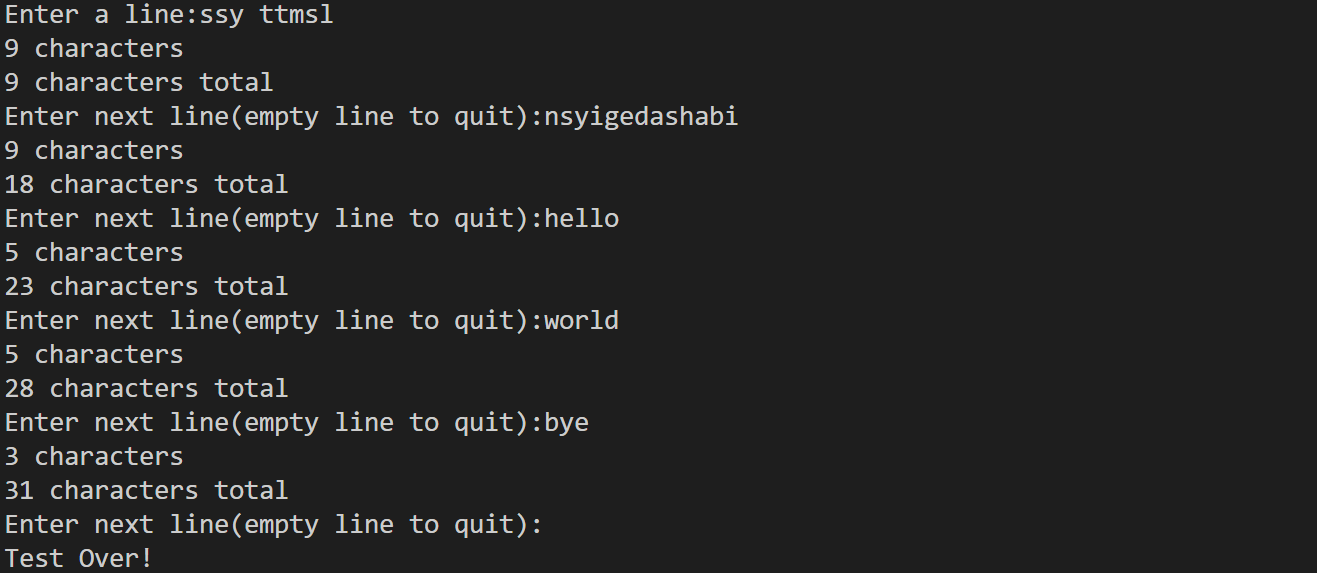
cout<<"Enter a line:";
cin.get(input,ArSize);//实际只会读取ArSize-1个char
while(cin)
{
cin.get(next);//读取缓冲区的换行符
while(next!='\n')//如果读取的不是换行符,说明读取的字符超出了Arsize-1的范围
{
cin.get(next);//则把超出范围的字符全部读掉,直到读到换行符
}
strcount(input);
cout<<"Enter next line(empty line to quit):";
cin.get(input,ArSize);
}
cout<<"Test Over!"<<endl;
return 0;
}
void strcount(const char *str)
{
static int total=0;//static在函数中定义的变量,只初始化一次,且在函数调用完后变量不会消失
int count=0;
while(*str++)//++的优先级更高,且先使用后自加,即先*str,再str+1
{
count++;
}
total+=count;
cout<<count<<" characters"<<endl;
cout<<total<<" characters total"<<endl;
}结果如下:
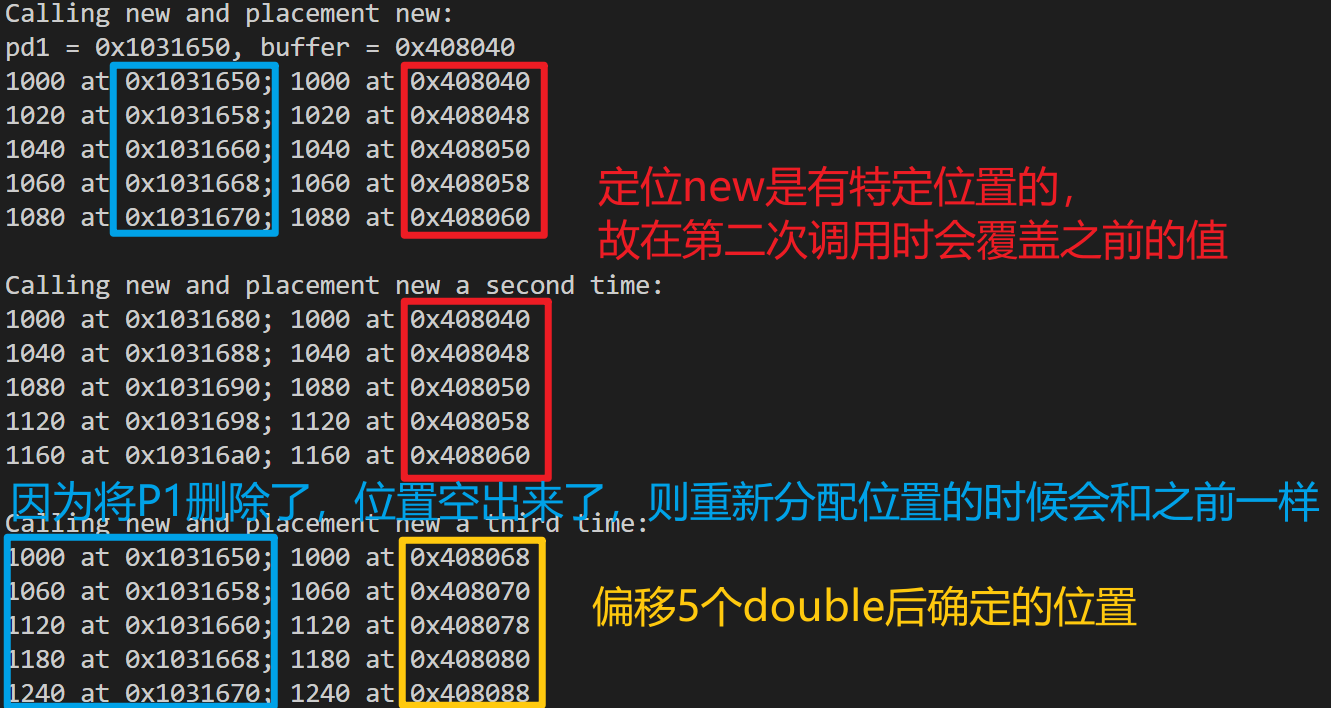
定位new运算符
首先需要包含头文件new,它提供了这种版本的new运算符的原型
#include<new>与常规的new使用相比,在new后面用(起始地址)指定new出空间的起始地址
- 定位new不能使用delete删除,只有常规new需要使用delete删除
1 |
|
结果如下:
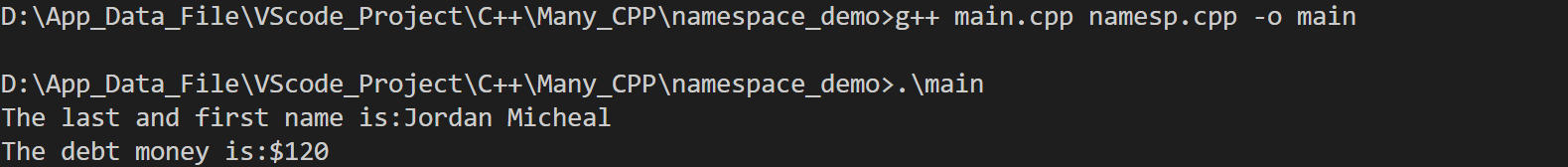
名称空间
- 使用新的关键字namespace创建名称空间
using 名称空间的名字::使用的名称空间中的某个内容//会将同名变量覆盖using namespace 名称空间的名字//此时引用区域可以使用该名称空间的所有内容,隐藏有变量 名称空间名字::变量- namesp.h
1 |
|
- namesp.cpp
1 |
|
- main.cpp
1 |
|
结果如下:
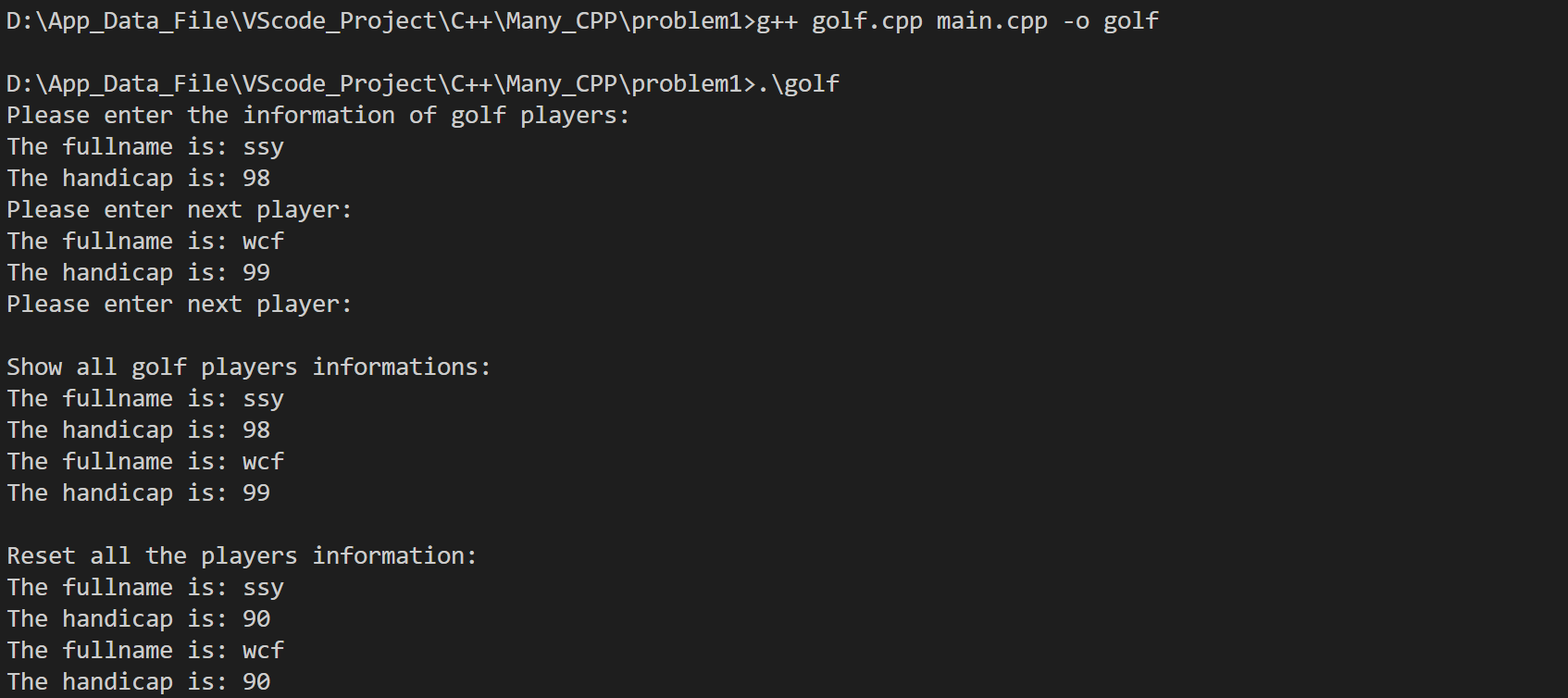
练习
1.多文件编译
存储高尔夫选手的姓名及成绩并显示,且能修改
golf.h
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
using namespace std;
const int Len = 40;
struct golf
{
char fullname[Len];
int handicap;
};
void setgolf(golf &g, const char *name, int hc);
int setgolf(golf &g);
void handicap(golf &g, int hc);
void showgolf(const golf &g);golf.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
void setgolf(golf &g, const char *name, int hc)
{
strcpy(g.fullname, name);
g.handicap = hc;
}
int setgolf(golf &g)
{
int temp = 1;
cout << "The fullname is: ";
cin.getline(g.fullname, Len);
if(strcmp(g.fullname, "") == 0)
{
temp = 0;
return temp;
}
else
{
cout << "The handicap is: ";
cin >> g.handicap;
cin.get();
return temp;
}
}
void handicap(golf &g, int hc)
{
g.handicap = hc;
}
void showgolf(const golf &g)
{
cout << "The fullname is: " << g.fullname << endl;
cout << "The handicap is: " << g.handicap << endl;
}main.c
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
using namespace std;
const int SIZE = 2;
int main(void)
{
golf g[SIZE];
int count = 0;
cout << "Please enter the information of golf players: " << endl;
while((count < SIZE) && (setgolf(g[count])))
{
cout << "Please enter next player: " << endl;
count++;
}
cout << "\nShow all golf players informations: " << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++)
showgolf(g[i]);
cout << "\nReset all the players information: " << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
handicap(g[i], 90);
showgolf(g[i]);
}
return 0;
}结果如下:
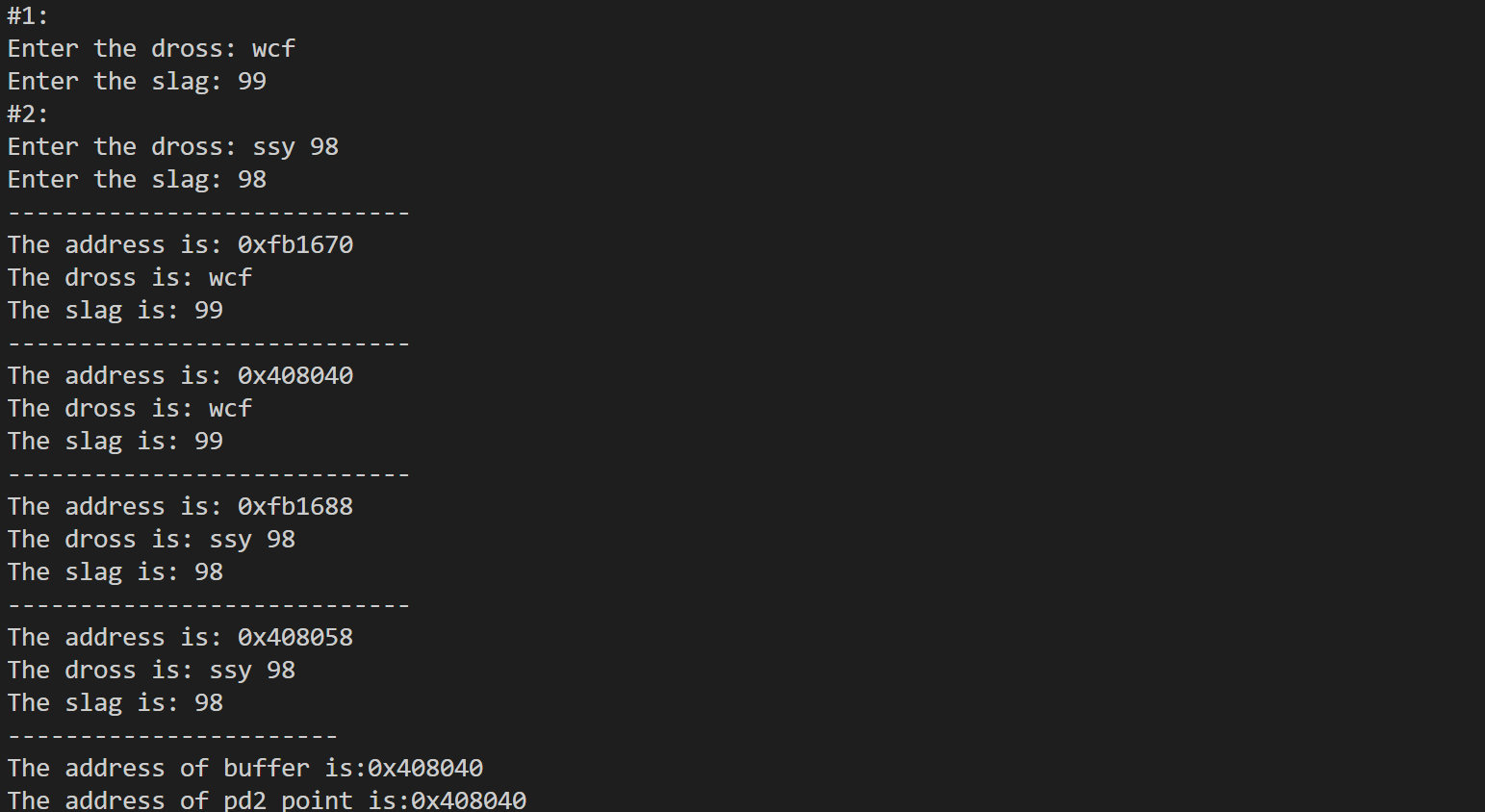
2.定位new运算符
- 体会普通new与定位new的区别
1 |
|
结果如下:
3.名称空间的使用
利用名称空间SALES求商品的平均值、最大值与最小值
p3.h
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
namespace SALES
{
const int QUARTERS = 4;
struct Sales
{
double sales[QUARTERS];
double average;
double max;
double min;
};
void setSales(Sales &s, const double ar[], int n);
void setSales(Sales &s);
void showSales(const Sales &s);
}p3.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
using namespace std;
namespace SALES
{
void setSales(Sales &s, const double ar[], int n)
{
double total = 0.0;
int i;
for(i = 0; i < n && i < 4; i++)
{
s.sales[i] = ar[i];
total += s.sales[i];
}
s.average = total / i;
s.max = s.sales[0];
s.min = s.sales[0];
for(int k = 1; k < i; k++)
{
s.max = (s.max > s.sales[k]) ? s.max : s.sales[k];
s.min = (s.min < s.sales[k]) ? s.min : s.sales[k];
}
if(n < 4)
{
for(int k = n; k < 4; k++)
s.sales[k] = 0;
}
}
void setSales(Sales &s)
{
double total = 0.0;
cout << "Enter 4 sales quarters: " << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < QUARTERS; i++)
{
cout << "#" << i+1 << ": ";
cin >> s.sales[i];
total += s.sales[i];
if(i == 0)
{
s.max = s.sales[i];
s.min = s.sales[i];
}
else
{
s.max = (s.max > s.sales[i]) ? s.max : s.sales[i];
s.min = (s.min < s.sales[i]) ? s.min : s.sales[i];
}
}
s.average = total / QUARTERS;
}
void showSales(const Sales &s)
{
cout << "Sales of 4 quarters: " << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < QUARTERS;i ++)
cout << s.sales[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << "Average = " << s.average << endl;
cout << "Max = " << s.max << endl;
cout << "Min = " << s.min << endl;
}
}main.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
using namespace SALES;
double ar[4] = {11.1, 22.2, 33.3, 44.4};
Sales sl;
setSales(sl, ar, 3);
showSales(sl);
setSales(sl);
showSales(sl);
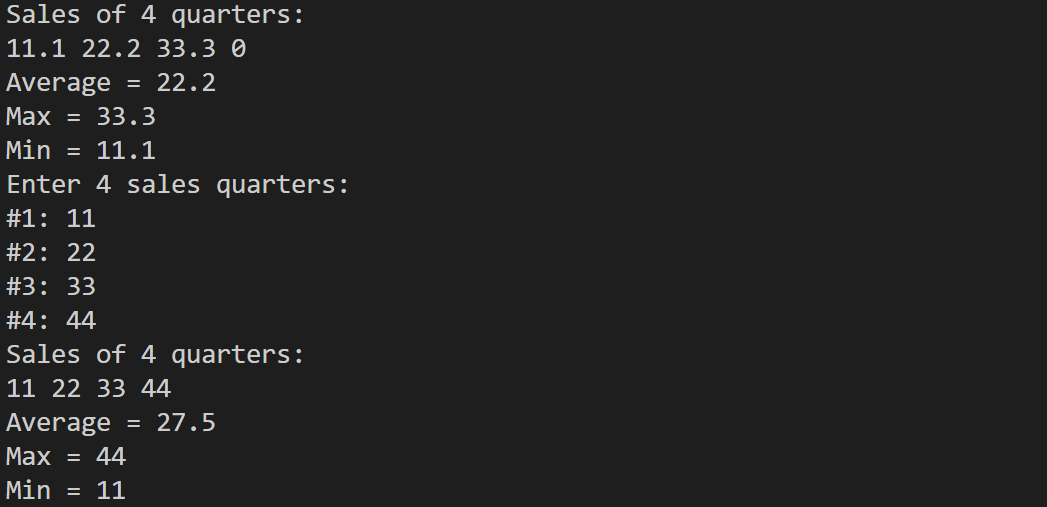
return 0;
}结果如下: