C++之函数……
函数与数组
1.参数传递
传递常规变量时,函数将使用该变量的拷贝;但传递数组时,函数将使用原来的数组
为将数组类型和元素个数告诉数组处理函数,需通过两个不同的参数来传递它们,一个是数组的首地址,一个是数组的大小
函数中的数组名实际上是一个指向数组的指针
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
using namespace std;
const int ArSize=8;
int sum_arr(int arr[],int size);
int main(void)
{
int cookies[ArSize]={1,2,4,8,16,32,64,128};
cout<<"cookies address:"<<cookies<<endl;
cout<<"size of cookies:"<<sizeof(cookies)<<endl;
int sum=sum_arr(cookies,ArSize);
cout<<"The sum of cookies is:"<<sum<<endl;
return 0;
}
int sum_arr(int arr[],int size)
{
int total=0;
cout<<"arr address:"<<arr<<endl;
cout<<"size of arr:"<<sizeof(arr)<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<size;i++)
{
total+=arr[i];
}
return total;
}结果如下:

2.数组与指针
参数入口有数组的函数的声明,通常用const修饰,这是为了在函数中无法通过指针修改数组中的值
例如下例中的
const double arr[]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
using namespace std;
const int Max=5;
int fill_array(double arr[],int size);
void show_array(const double arr[],int size);
int main(void)
{
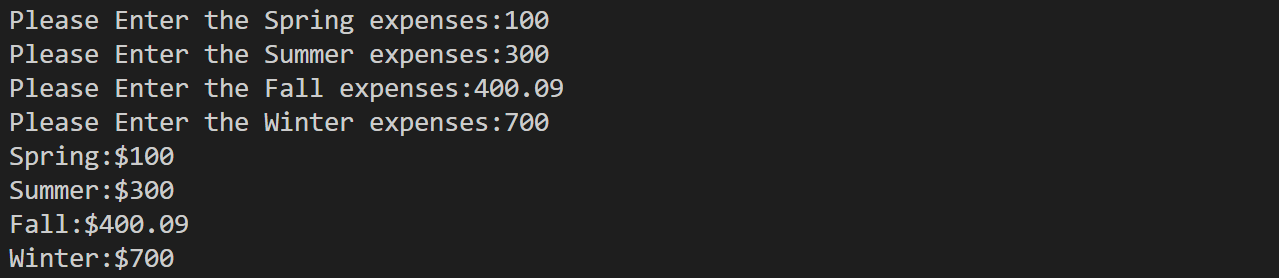
double properties[Max];
int number=fill_array(properties,Max);//number表示成功输入的个数
show_array(properties,number);
return 0;
}
int fill_array(double arr[],int size)
{
double temp;
int i;
for(i=0;i<size;i++)
{
cout<<"Enter value #"<<i+1<<":";
cin>>temp;
if(!cin)//当输入出现错误:类型不匹配
{
cin.clear();
while(cin.get()!='\n');
cout<<"Bad input:input process terminated!"<<endl;
break;
}
else if(temp<0)
{
break;
}
else
arr[i]=temp;
}
return i;
}
void show_array(const double arr[],int size)
{
cout<<"-------------------"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<size;i++)
{
cout<<"Property #"<<i+1<<":$"<<arr[i]<<endl;
}
}结果如下:

3.使用数组区间的函数
1 |
|
结果如下:
1 | The sum of cookies is:255 |
函数与C-type字符串
函数的参数入口传递的是C-type字符串时,传入的值也是地址,即将地址传给了指针
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
using namespace std;
unsigned int ch_number(const char *arr,char ch);
int main(void)
{
char c_array[]="milmimm";
const char *pt="uloinuu";
unsigned int m=ch_number(c_array,'m');
unsigned int u=ch_number(pt,'u');
cout<<"m happens "<<m<<" times"<<endl;
cout<<"u happens "<<u<<" times"<<endl;
return 0;
}
unsigned int ch_number(const char *arr,char ch)
{
unsigned int count=0;
while(*arr)
{
if(*arr==ch)
count++;
arr++;
}
return count;
}结果如下:

函数返回字符串时返回的是地址
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
using namespace std;
char *buildstr(char ch,int n);
int main(void)
{
char ch;
int times;
cout<<"Enther a character:";
cin>>ch;
cout<<"Enter an integer:";
cin>>times;
char *pt=buildstr(ch,times);
cout<<pt<<endl;
delete [] pt;
return 0;
}
char *buildstr(char ch,int n)
{
char *pt=new char[n+1];
pt[n]='\0';
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
pt[i]=ch;
}
return pt;
}结果如下:

函数与结构体
直接将结构体的名字当成一个数据类型,像传递整数等其他正常数据类型一样操作就行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
using namespace std;
//实现将直角坐标转化为极坐标
struct polar
{
double distance;
double angle;
};
struct rect
{
double x;
double y;
};
polar rect_to_polar(rect xypos);
void show_polar(polar pplace);
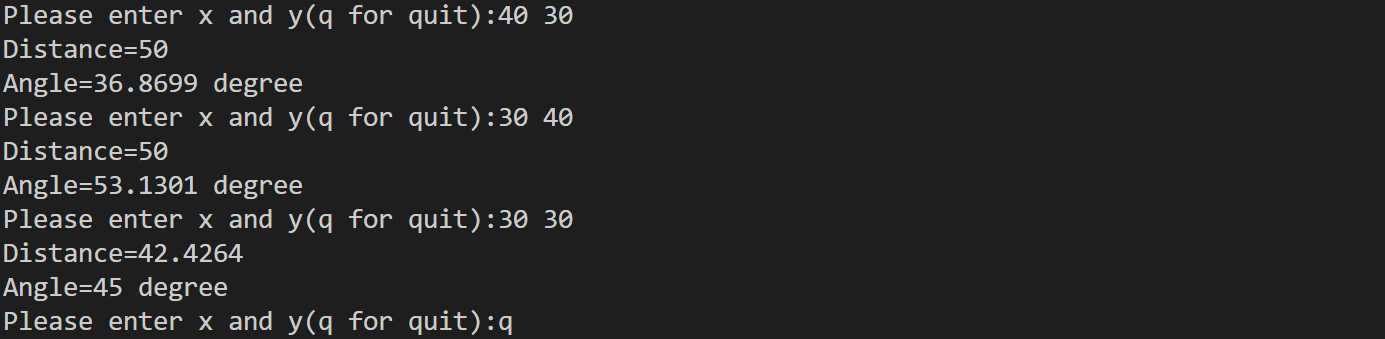
int main(void)
{
rect rplace;
polar pplace;
cout<<"Please enter x and y(q for quit):";
while(cin>>rplace.x>>rplace.y)
{
pplace=rect_to_polar(rplace);
show_polar(pplace);
cout<<"Please enter x and y(q for quit):";
}
return 0;
}
polar rect_to_polar(rect xypos)
{
polar pplace;
pplace.distance=sqrt(xypos.x*xypos.x+xypos.y*xypos.y);
pplace.angle=atan2(xypos.y,xypos.x);//返回的是弧度制
return pplace;
}
void show_polar(polar pplace)
{
const double Rad_to_deg=57.29577951;
cout<<"Distance="<<pplace.distance<<endl;
//将弧度制转化为角度制
cout<<"Angle="<<pplace.angle*Rad_to_deg<<" degree"<<endl;
}结果如下:

通常需要传递结构体的地址而不是整个结构体以节省时间和空间,故使用指向结构体的指针来传递参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
using namespace std;
//实现将直角坐标转化为极坐标
struct polar
{
double distance;
double angle;
};
struct rect
{
double x;
double y;
};
void rect_to_polar(const rect *pxy,polar *pda);
void show_polar(const polar *pda);
int main(void)
{
rect rplace;
polar pplace;
cout<<"Please enter x and y(q for quit):";
while(cin>>rplace.x>>rplace.y)
{
rect_to_polar(&rplace,&pplace);
show_polar(&pplace);
cout<<"Please enter x and y(q for quit):";
}
return 0;
}
void rect_to_polar(const rect *pxy,polar *pda)
{
pda->distance=sqrt(pxy->x*pxy->x+pxy->y*pxy->y);
pda->angle=atan2(pxy->y,pxy->x);//返回的是弧度制
}
void show_polar(const polar *pda)
{
const double Rad_to_deg=57.29577951;
cout<<"Distance="<<pda->distance<<endl;
//将弧度制转化为角度制
cout<<"Angle="<<pda->angle*Rad_to_deg<<" degree"<<endl;
}结果如下:
函数与string对象
1 |
|
结果如下:

函数与array对象
- 在函数中对array对象进行传递时,若直接将array对象的名字传递给函数,那么传递的将是array对象的复制版本,并不是直接改变了array对象里面的值,所以下面例子中使用传递地址的方式对数据进行写入操作
- 指向array对象的指针不能直接通过指针pa[i]去改变array对象中的值,只能通过
(*pa)[i]的方式去访问array对象中的值 - 函数中参数的形式为:
array<double,Seasons> *pa - 其实有点类似于函数与结构体的使用,只是array对象不存在->与.的使用方式,但都可以通过(*pa)访问指针指向的对象
1 |
|
结果如下:
递归
1 |
|
结果如下:

函数指针
函数指针:
double (*pt)(int),可以指向输入参数为一个整数,输出为double类型的函数在函数中用
(*pt)表示对应函数1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
using namespace std;
double Jack(int L);
double Rick(int L);
void computes(int L,double (*pt)(int));
int main(void)
{
int lines;
cout<<"Please enter the Lines:";
cin>>lines;
cout<<"The times computes by Jack is:";
computes(lines,Jack);
cout<<"The times computes by Rick is:";
computes(lines,Rick);
return 0;
}
double Jack(int L)
{
return L*0.05;
}
double Rick(int L)
{
return L*0.03+0.0004*L*L;
}
void computes(int L,double (*pt)(int))
{
cout<<(*pt)(L)<<" seconds"<<endl;
}结果如下:

若想表达指向数组(数组中的元素为指向函数的指针)的指针:则例如
const double *(*(*pd)[3])(const double *,int)=&pa;,其中(*pd)表示指针,[3]表示指向的是一个数组,*(*pd)[3]表示指向一个数组中有3个元素(每个元素为指向函数的指针)的指针,可以理解为指向指针的指针下例中:
const double *(*(*pd)[3])(const double *,int)=&pa的&pa为取数组pa整体的首地址1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
using namespace std;
const double *f1(const double *ar,int n);
const double *f2(const double ar[],int n);
const double *f3(const double ar[],int n);
int main(void)
{
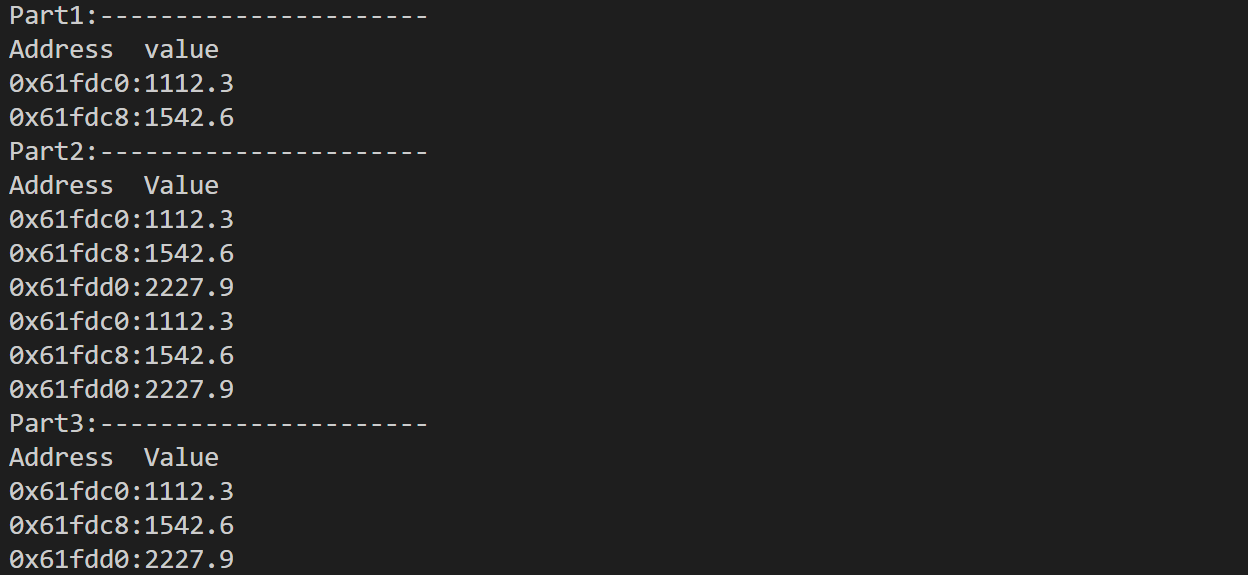
double av[3]={1112.3,1542.6,2227.9};
//Part1:
//p1(p2):pointer to a function
const double *(*p1)(const double *,int)=f1;
auto p2=f2;//编译器会根据f2的值自己得出p2的数据类型,并将f2赋值给p2
cout<<"Part1:----------------------"<<endl;
cout<<"Address\t value"<<endl;
cout<<(*p1)(av,3)<<":"<<*((*p1)(av,3))<<endl;//这里*((*p1)(av,3))不加最外层括号也可以,因为()的优先级高于*
cout<<p2(av,3)<<":"<<*p2(av,3)<<endl;//*pt也可以直接用pt表示,故这里p2用最简单的形式表示出来了
//Part2:
//pa(pb) is an array of pointers
const double *(*pa[3])(const double *,int)={f1,f2,f3};
auto pb=pa;
cout<<"Part2:----------------------"<<endl;
cout<<"Address\t Value"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
cout<<pa[i](av,3)<<":"<<*pa[i](av,3)<<endl;
}
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
cout<<pb[i](av,3)<<":"<<*pb[i](av,3)<<endl;
}
//Part3:
//pc(pd) is a pointer to an array of function pointers
auto pc=&pa;
const double *(*(*pd)[3])(const double *,int)=&pa;
cout<<"Part3:----------------------"<<endl;
cout<<"Address\t Value"<<endl;
cout<<(*pc)[0](av,3)<<":"<<*(*pc)[0](av,3)<<endl;
const double *pdb=(*pd)[1](av,3);
cout<<pdb<<":"<<*pdb<<endl;
cout<<(*(*pd)[2])(av,3)<<":"<<*(*(*pd)[2])(av,3)<<endl;
return 0;
}
const double *f1(const double *ar,int n)
{
return ar;
}
const double *f2(const double ar[],int n)
{
return ar+1;
}
const double *f3(const double ar[],int n)
{
return ar+2;
}结果如下:
使用
typedef const double *(*p1)(const double *,int)后p1称为了指代此函数指针的数据类型
