本节主要介绍了TensorFlow基础知识中与张量(Tensor)相关的部分,包括创建张量、张量运算、维度变换等
创建张量
- TensorFlow的定义:An end-to-end open source machine learning platform
- TensorFlow中的”Tensor”表示张量,其实就是多维数组
1.张量的基本创建
tf.constant(value,dtype,shape)value可以是数字、python列表、numpy数组、bool类型、字符串
dtype:(可省略)
| 数据类型 | 描述 |
| —————— | ————————————————- |
| tf.int8 | 8位有符号整数 |
| tf.int16 | 16位有符号整数 |
| tf.int32 | 32位有符号整数 |
| tf.int64 | 64位有符号整数 |
| tf.uint8 | 8位无符号整数 |
| tf.float32 | 32位浮点数 |
| tf.float64 | 64位浮点数 |
| tf.string | 字符串(非Unicode编码的字节数组) |
| tf.bool | 布尔型 |
| tf.complex64 | 复数,实数和虚数分别为32位浮点数 |shape:张量的形状(可省略)
创建Tensor对象
1 | #创建张量 |
结果如下:
<tf.Tensor: shape=(2, 2), dtype=int32, numpy=
array([[1, 2],
[3, 4]])>
使用张量.numpy()方法
1 | #使用张量.numpy()方法 |
结果如下:
[[1 2]
[3 4]]
------------------------------
tf.Tensor(
[[1 2]
[3 4]], shape=(2, 2), dtype=int32)
------------------------------
<class 'tensorflow.python.framework.ops.EagerTensor'>
参数为数字时,shape=()
1 | #参数为数字时,shape=() |
结果如下:
1 | tf.Tensor(1.0, shape=(), dtype=float32) |
参数为NumPy数组
- numpy创建浮点数数组时,默认的浮点型是64位浮点数
- 当使用numpy数组创建张量时,TensorFlow会接受数组元素的数据类型,使用64位浮点数保存数据
1 | #参数为Numpy数组 |
结果如下:
tf.Tensor(
[[1 2]
[3 4]], shape=(2, 2), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(
[[1. 2.]
[3. 4.]], shape=(2, 2), dtype=float64)
参数为字符串
1 | #参数为字符串 |
结果如下:
<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=string, numpy=b'hello'>
2.改变张量中元素的数据类型
tf.cast(x,dtype)#将返回一个张量对象
1 | #改变张量中元素的数据类型 |
结果如下:
<tf.Tensor: shape=(2, 2), dtype=float32, numpy=
array([[1., 2.],
[3., 4.]], dtype=float32)>
3.创建张量的其他函数
tf.convert_to_tensor(数组/列表/数字/布尔型/字符串)
1 | #其他创建张量的函数 |
结果如下:
<class 'tensorflow.python.framework.ops.EagerTensor'>
4.判断是否为张量
tf.is_tensor(a)isinstance(a,tf.Tensor)
1 | #判断是否为张量 |
结果如下:
True
False
True
True
5.创建全0张量和全1张量
- 全0张量:
tf.zero(shape,dtype=tf.float32) - 全1张量:
tf.ones(shape,dtype=tf.float32)
1 | #创建全0张量和全1张量 |
结果如下:
tf.Tensor(
[[0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0.]], shape=(3, 4), dtype=float32)
tf.Tensor([[0 0]], shape=(1, 2), dtype=int32)
6.创建元素值都相同的张量
tf.fill(dims,value)- dims:形状
- value:为要填充的值,根据此值确定数据类型
1 | #常见元素值都相同的张量 |
结果如下:
tf.Tensor(
[[6 6 6]
[6 6 6]], shape=(2, 3), dtype=int32)
----------------------------------------
tf.Tensor(
[[6. 6. 6.]
[6. 6. 6.]], shape=(2, 3), dtype=float32)
7.创建随机数张量
- 正态分布:
tf.random.normal(shape,mean,stddev,dtype)- mean:均值,默认为0
- stddev:标准差,默认为1
- dtype:数据类型,默认为float32
- 截断正态分布:
tf.random.truncated_normal(shape,mean,stddev,dtype)- 返回一个截断的正态分布
- 截断的标准是2倍的标准差
- 设置随机种子:
tf.random.set_seed()#seed相同,产生的张量相同 - 均匀分布:
tf.random.uniform(shape,minval,maxval,dtype)#maxval为开区间 - 随机打乱:
tf.random.shuffle()#只打乱第一个维度的数据
1 | #创建随机数张量 |
结果如下:
tf.Tensor(
[[ 0.8266079 0.7237875 0.3424334 0.49157178 -0.37519592 1.1376799 ]
[-0.5669446 -0.3625808 1.5405077 0.6373274 -1.9455124 -0.7011395 ]
[ 1.2457833 -0.39937112 0.57883924 1.0344775 -0.6350136 -1.3593744 ]
[-0.74130106 1.8143122 0.5292364 -0.10480234 -1.7358512 -0.3791651 ]
[ 0.5712524 0.9349497 -0.22174385 -0.59780544 0.78962743 0.5501346 ]
[ 0.9522022 0.14572807 -0.21552448 1.7505981 -0.76506436 -2.3946 ]], shape=(6, 6), dtype=float32)
tf.Tensor(
[[ 0.36231953 -0.12280609 -1.0638309 -0.37071744 -0.73713136 1.2813414 ]
[ 0.87333363 -1.4310946 -0.47064283 0.12014091 -0.92487514 1.3596456 ]
[ 1.2385474 0.07997006 -0.07874179 0.13667127 0.44561246 -1.7509358 ]
[-0.24318981 -0.09602328 1.65389 1.7249115 -0.5238166 0.24563125]
[ 1.4265472 -0.01189587 0.2186302 -0.42843634 0.5324539 0.24380386]
[-1.2853507 -1.6559658 0.54867435 -0.6609358 0.7402121 1.3007758 ]], shape=(6, 6), dtype=float32)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
tf.Tensor(
[[1 8 1]
[0 8 4]
[3 1 6]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=int32)
----------------------------------------
tf.Tensor(
[[1 2]
[5 6]
[3 4]], shape=(3, 2), dtype=int32)
----------------------------------------
8.创建整数序列
tf.range(start,limit,delta=1,dtype)- start可省略,默认为0
- limit不可省略,为开区间
- delta为步长,默认为1,可省略
1 | #创建整数序列 |
结果如下:
tf.Tensor([1 3 5 7 9], shape=(5,), dtype=int32)
9.Tensor对象的属性
.ndim:维度.shape:形状.dtype:类型tf.shape(a):形状tf.size(a):总数tf.rank(a):维度
1 | #Tensor对象的属性 |
结果如下:
The nidm: 2
The shape: (2, 2)
The dtype: <dtype: 'int32'>
---------------------------------------------
The tf.size: tf.Tensor(4, shape=(), dtype=int32)
The tf.shape: tf.Tensor([2 2], shape=(2,), dtype=int32)
The tf.rank: tf.Tensor(2, shape=(), dtype=int32)
维度变换
1.改变张量形状
tf.reshape(tensor,shape)
1 | #改变张量形状 |
结果如下:
tf.Tensor([[1 2 3 4]], shape=(1, 4), dtype=int32)
------------------------------------------------
tf.Tensor(
[[1 2]
[3 4]], shape=(2, 2), dtype=int32)
2.增加和删除维度
- 增加:
tf.expand_dims(input,axis)#增加的维度长度为1 - 删除:
tf.squeeze(input,axis)#只能删除长度为1的维度,若不指定axis,则删除所有长度为1的轴
1 | #增强和删除维度 |
结果如下:
tf.Tensor(
[[[ 0 1 2 3 4 5]]
[[ 6 7 8 9 10 11]]
[[12 13 14 15 16 17]]
[[18 19 20 21 22 23]]], shape=(4, 1, 6), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(
[[ 0 1 2 3 4 5]
[ 6 7 8 9 10 11]
[12 13 14 15 16 17]
[18 19 20 21 22 23]], shape=(4, 6), dtype=int32)
3.交换维度
tf.transpose(a,perm)#perm根据axis指定交换的顺序
1 | #交换维度 |
结果如下:
tf.Tensor(
[[[ 0 1 2 3]
[12 13 14 15]]
[[ 4 5 6 7]
[16 17 18 19]]
[[ 8 9 10 11]
[20 21 22 23]]], shape=(3, 2, 4), dtype=int32)
4.拼接与分割
- 拼接:
tf.concat(tensors,axis)- tensors:为所有需要拼接的张量列表
- axis:指定在哪个轴上拼接
- 分割:
tf.split(value,num_or_size_split,axis=0)
1 | #拼接与分割 |
结果如下:
tf.Tensor(
[[ 0 1 2 3 4 5]
[ 6 7 8 9 10 11]
[12 13 14 15 16 17]
[18 19 20 21 22 23]
[ 0 1 2 3 4 5]
[ 6 7 8 9 10 11]
[12 13 14 15 16 17]
[18 19 20 21 22 23]], shape=(8, 6), dtype=int32)
--------------------------------------------------
tf.Tensor(
[[ 0 1 2 3 4 5 0 1 2 3 4 5]
[ 6 7 8 9 10 11 6 7 8 9 10 11]
[12 13 14 15 16 17 12 13 14 15 16 17]
[18 19 20 21 22 23 18 19 20 21 22 23]], shape=(4, 12), dtype=int32)
------------------------------------------------------------
tf.Tensor(
[[ 0 1 2 3 4 5]
[ 6 7 8 9 10 11]], shape=(2, 6), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor([[12 13 14 15 16 17]], shape=(1, 6), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor([[18 19 20 21 22 23]], shape=(1, 6), dtype=int32)
5.堆叠与分解
- 堆叠:
tf.stack(values,axis) - 分解:
tf.unstack(values,axis)
1 | #堆叠与分解 |
结果如下:
tf.Tensor(
[[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]], shape=(2, 3), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(
[[1 4]
[2 5]
[3 6]], shape=(3, 2), dtype=int32)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[<tf.Tensor: shape=(6,), dtype=int32, numpy=array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5])>, <tf.Tensor: shape=(6,), dtype=int32, numpy=array([ 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11])>, <tf.Tensor: shape=(6,), dtype=int32, numpy=array([12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17])>, <tf.Tensor: shape=(6,), dtype=int32, numpy=array([18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23])>]
部分采样
tf.gather(params,axis,indices)#用一个索引列表,将给定张量中,对应索引值的元素提取出来,但一次只能索引一个维度tf.gather_nd(params,indices)#可同时采样多个点
1 | #部分采样 |
结果如下:
tf.Tensor(
[[ 0 1 2 3 4 5]
[ 6 7 8 9 10 11]
[12 13 14 15 16 17]
[18 19 20 21 22 23]], shape=(4, 6), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(
[[ 0 1 2 3 4 5]
[ 6 7 8 9 10 11]
[18 19 20 21 22 23]], shape=(3, 6), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(
[[ 0 1 3]
[ 6 7 9]
[12 13 15]
[18 19 21]], shape=(4, 3), dtype=int32)
----------------------------------------
tf.Tensor([ 0 7 14 21], shape=(4,), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(
[[ 0 1 2 3 4 5]
[ 6 7 8 9 10 11]
[12 13 14 15 16 17]], shape=(3, 6), dtype=int32)
张量运算
1.基本数学运算
加减乘法运算
| 算数操作 | 描述 |
| ————————- | ———————— |
| tf.add(x,y) | 将x和y逐元素相加 |
| tf.substract(x,y) | 将x和y逐元素相减 |
| tf.multiply(x,y) | 将x和y逐元素相乘 |
| tf.divide(x,y) | 将x和y逐元素相除 |
| tf.math.mode(x,y) | 对x逐元素 |幂指对数运算
| 算数操作 | 描述 |
| ——————— | ————————————————————————— |
| tf.pow(x,y) | 对x求y的幂次方(当y为小数时,x需为浮点数) |
| tf.square(x) | 对x逐元素求平方 |
| tf.sqrt(x) | 对x逐元素开平方根 |
| tf.exp(x) | 计算e的x次方(要求x为浮点数,且必须是float64) |
| tf.math.log(x) | 计算自然对数,底数为e(要求x为浮点数) |其他运算
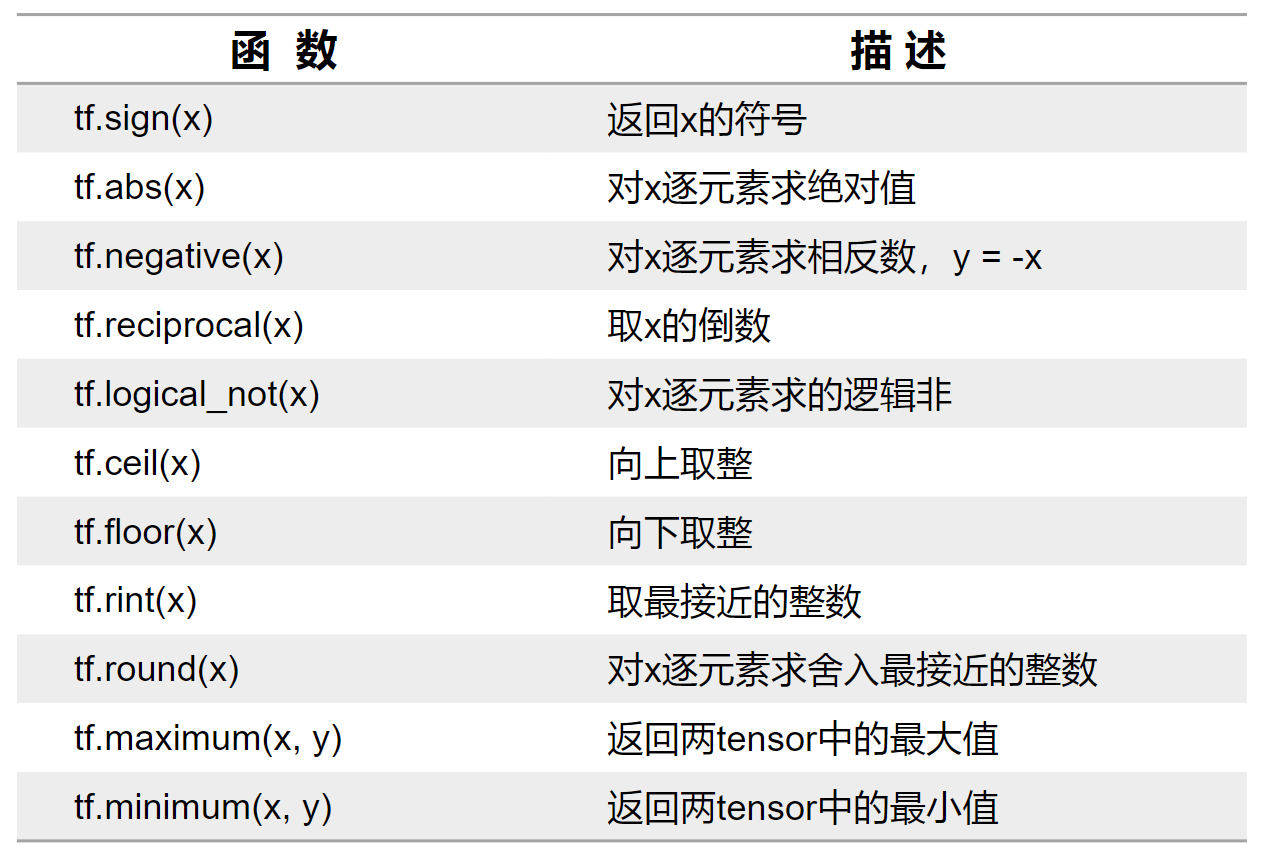
三角函数和反三角函数运算
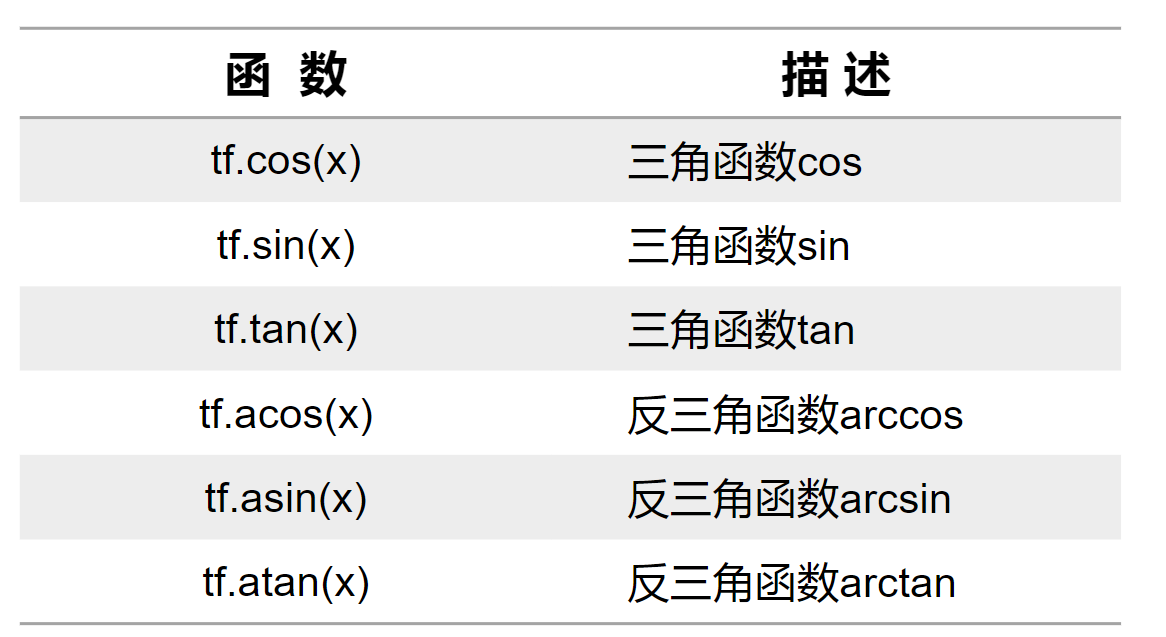
重载运算符
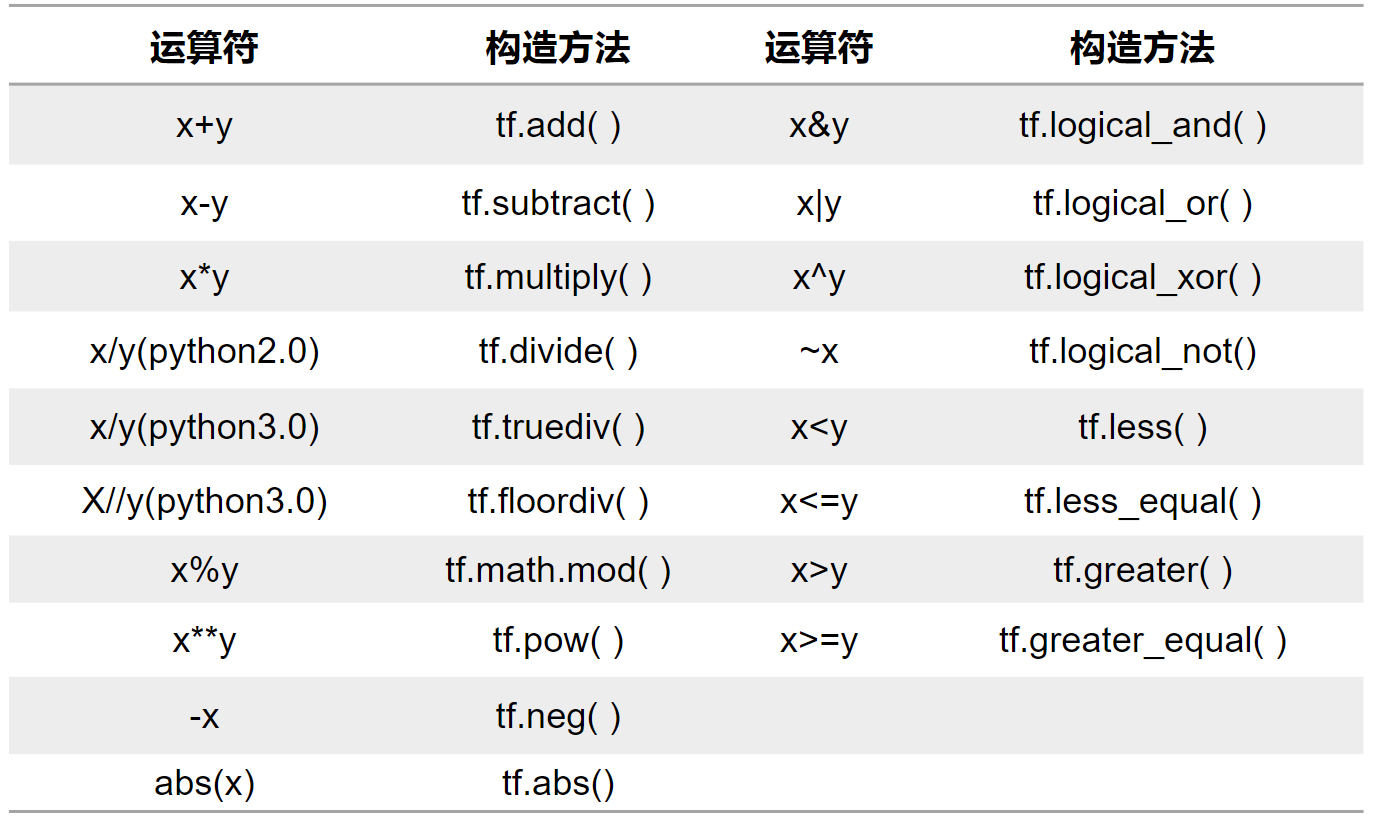
2.向量乘法
tf.matmul(a,b)a @ b
1 | #多维向量乘法 |
结果如下:
tf.Tensor(
[[[ 2.203142 0.09738441 1.9606446 -1.1057658 ]
[-0.27357578 0.14026386 0.94474745 2.1895509 ]
[ 1.7446913 -0.9555952 -0.04033652 1.8337672 ]]
[[-1.0159464 0.11673293 -0.04575142 0.06979337]
[-1.342845 1.4855313 1.4126754 -0.32664305]
[ 3.1746514 -1.7697542 -1.3596829 2.2296028 ]]], shape=(2, 3, 4), dtype=float32)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
tf.Tensor(
[[[ 0 1 2]
[ 3 4 5]]
[[ 6 7 8]
[ 9 10 11]]], shape=(2, 2, 3), dtype=int32)
*********************************************
tf.Tensor(
[[[ 0 1]
[ 2 3]
[ 4 5]]
[[ 6 7]
[ 8 9]
[10 11]]], shape=(2, 3, 2), dtype=int32)
*********************************************
tf.Tensor(
[[[ 10 13]
[ 28 40]]
[[172 193]
[244 274]]], shape=(2, 2, 2), dtype=int32)
3.数据统计
| 函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| tf.reduce_sum(input_tensor,axis) | 求和,axis未指定时默认求全局 |
| tf.reduce_mean(input_tensor,axis) | 求平均值,axis未指定时默认求全局 |
| tf.reduce_max(input_tensor,axis) | 求最大值,axis未指定时默认求全局 |
| tf.reduce_min(input_tensor,axis) | 求最小值,axis未指定时默认求全局 |
| tf.argmax(input_tensor,axis) | 求最大值索引,axis默认为0 |
| tf.argmin(input_tensor,axis) | 求最小值索引,axis默认为0 |
