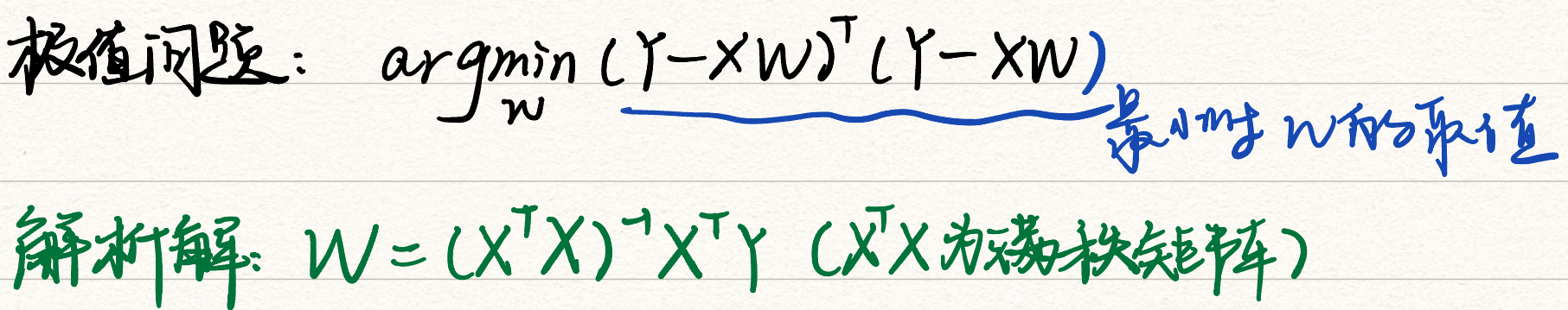本节主要介绍了如何通过解析法与梯度下降法求解线性回归问题。
解析法实现一元线性回归
加载样本数据:x、y
学习模型:计算w、b
预测:y_pred=w*x_test+b
1.纯Python实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 x=[137.97 ,104.50 ,100.00 ,124.32 ,79.20 ,99.00 ,124.00 ,114.00 ,106.69 ,138.05 ,53.75 ,46.91 ,68.00 ,63.02 ,81.26 ,86.21 ] y=[145.00 ,110.00 ,93.00 ,116.00 ,65.32 ,104.00 ,118.00 ,91.00 ,62.00 ,133.00 ,51.00 ,45.00 ,78.50 ,69.65 ,75.69 ,95.30 ] x_mean=sum (x)/len (x) y_mean=sum (y)/len (y) sumXY=0.0 sumX=0.0 for i in range (len (x)): sumXY+=(x[i]-x_mean)*(y[i]-y_mean) sumX+=pow ((x[i]-x_mean),2 ) w=sumXY/sumX b=y_mean-w*x_mean print ("w:" ,w)print ("b:" ,b)x_test=[128.15 ,45.00 ,141.43 ,106.27 ,99.00 ,53.84 ,85.36 ,70.00 ] for i in range (len (x_test)): print ("The Y of" ,x_test[i],'is:' ,w*x_test[i]+b)
结果如下:
w: 0.8945605120044221
b: 5.410840339418002
The Y of 128.15 is: 120.0487699527847
The Y of 45.0 is: 45.66606337961699
The Y of 141.43 is: 131.92853355220342
The Y of 106.27 is: 100.47578595012793
The Y of 99.0 is: 93.97233102785579
The Y of 53.84 is: 53.57397830573609
The Y of 85.36 is: 81.77052564411547
The Y of 70.0 is: 68.03007617972756
2.NumPy实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 import numpy as npx=np.array([137.97 ,104.50 ,100.00 ,124.32 ,79.20 ,99.00 ,124.00 ,114.00 ,106.69 ,138.05 ,53.75 ,46.91 ,68.00 ,63.02 ,81.26 ,86.21 ]) y=np.array([145.00 ,110.00 ,93.00 ,116.00 ,65.32 ,104.00 ,118.00 ,91.00 ,62.00 ,133.00 ,51.00 ,45.00 ,78.50 ,69.65 ,75.69 ,95.30 ]) x_mean=np.mean(x) y_mean=np.mean(y) sumXY=np.sum ((x-x_mean)*(y-y_mean)) sumX=np.sum ((x-x_mean)**2 ) w=sumXY/sumX b=y_mean-w*x_mean print ("w:" ,w)print ("b:" ,b)x_test=np.array([128.15 ,45.00 ,141.43 ,106.27 ,99.00 ,53.84 ,85.36 ,70.00 ]) Y=w*x_test+b print ("The Y is:" ,Y)
结果如下:
w: 0.894560512004422
b: 5.410840339418002
The Y is: [120.04876995 45.66606338 131.92853355 100.47578595 93.97233103
53.57397831 81.77052564 68.03007618]
3.TensorFlow实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 import tensorflow as tfx=tf.constant([137.97 ,104.50 ,100.00 ,124.32 ,79.20 ,99.00 ,124.00 ,114.00 ,106.69 ,138.05 ,53.75 ,46.91 ,68.00 ,63.02 ,81.26 ,86.21 ]) y=tf.constant([145.00 ,110.00 ,93.00 ,116.00 ,65.32 ,104.00 ,118.00 ,91.00 ,62.00 ,133.00 ,51.00 ,45.00 ,78.50 ,69.65 ,75.69 ,95.30 ]) x_mean=tf.reduce_mean(x) y_mean=tf.reduce_mean(y) sumXY=tf.reduce_sum((x-x_mean)*(y-y_mean)) sumX=tf.reduce_sum((x-x_mean)**2 ) w=sumXY/sumX b=y_mean-w*x_mean print ("w:" ,w.numpy())print ("b:" ,b.numpy())x_test=tf.constant([128.15 ,45.00 ,141.43 ,106.27 ,99.00 ,53.84 ,85.36 ,70.00 ]) Y=w*x_test+b print ("The Y is:" ,Y.numpy())
结果如下:
w: 0.8945604
b: 5.4108505
The Y is: [120.04876 45.66607 131.92853 100.475784 93.97233 53.573982
81.77052 68.030075]
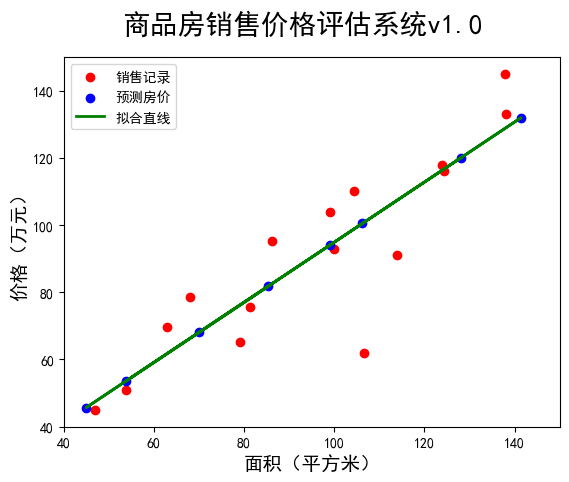
4.数据和模型可视化 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 import numpy as npimport tensorflow as tfimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltx=tf.constant([137.97 ,104.50 ,100.00 ,124.32 ,79.20 ,99.00 ,124.00 ,114.00 ,106.69 ,138.05 ,53.75 ,46.91 ,68.00 ,63.02 ,81.26 ,86.21 ]) y=tf.constant([145.00 ,110.00 ,93.00 ,116.00 ,65.32 ,104.00 ,118.00 ,91.00 ,62.00 ,133.00 ,51.00 ,45.00 ,78.50 ,69.65 ,75.69 ,95.30 ]) x_mean=tf.reduce_mean(x) y_mean=tf.reduce_mean(y) sumXY=tf.reduce_sum((x-x_mean)*(y-y_mean)) sumX=tf.reduce_sum((x-x_mean)**2 ) w=sumXY/sumX b=y_mean-w*x_mean print ("线性模型:y={}*x+{}" .format (w.numpy(),b.numpy()))x_test=np.array([128.15 ,45.00 ,141.43 ,106.27 ,99.00 ,53.84 ,85.36 ,70.00 ]) Y=(w*x_test+b).numpy() print ("面积\t房价" )for i in range (len (x_test)): print (x_test[i],"\t" ,round (Y[i],2 )) plt.figure(num="一维线性回归数据可视化" ) plt.rcParams["font.sans-serif" ]="SimHei" plt.rcParams["axes.unicode_minus" ]=False plt.scatter(x,y,color="red" ,label="销售记录" ) plt.scatter(x_test,Y,color="blue" ,label="预测房价" ) plt.plot(x_test,Y,color="green" ,label="拟合直线" ,linewidth=2 ) plt.xlabel("面积(平方米)" ,fontsize=14 ) plt.ylabel("价格(万元)" ,fontsize=14 ) plt.xlim(40 ,150 ) plt.ylim(40 ,150 ) plt.suptitle("商品房销售价格评估系统v1.0" ,fontsize=20 ) plt.legend(loc=2 ) plt.show()
结果如下:
线性模型:y=0.8945603966712952*x+5.410850524902344
面积 房价
128.15 120.05
45.0 45.67
141.43 131.93
106.27 100.48
99.0 93.97
53.84 53.57
85.36 81.77
70.0 68.03
解析法实现多元线性回归
加载样本数据
数据处理:将输入的数据转化为模型要求的形式
学习模型:计算W
预测:Y=X@W
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 import numpy as npx1=np.array([137.97 ,104.50 ,100.00 ,124.32 ,79.20 ,99.00 ,124.00 ,114.00 ,106.69 ,138.05 ,53.75 ,46.91 ,68.00 ,63.02 ,81.26 ,86.21 ]) x2=np.array([3 ,2 ,2 ,3 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,2 ,2 ,3 ,1 ,1 ,1 ,1 ,2 ,2 ]) y=np.array([145.00 ,110.00 ,93.00 ,116.00 ,65.32 ,104.00 ,118.00 ,91.00 ,62.00 ,133.00 ,51.00 ,45.00 ,78.50 ,69.65 ,75.69 ,95.30 ]) x0=np.ones(len (x1)) X=np.stack([x0,x1,x2],axis=1 ) print ("The X is:\n" ,X)Y=y.reshape(-1 ,1 ) print ("The Y is:\n" ,Y)Xt=np.transpose(X) XtX_1=np.linalg.inv(np.matmul(Xt,X)) XtX_1_Xt=np.matmul(XtX_1,Xt) W=np.matmul(XtX_1_Xt,Y) print ("The W is:\n" ,W)W=W.reshape(-1 ) print ("多元线性回归方程:Y={}*x1+{}*x2+{}" .format (W[1 ],W[2 ],W[0 ]))print ("请输入房屋面积和房间数,预测房屋销售价格:" )x1_test=float (input ("商品房面积:" )) x2_test=float (input ("房间数:" )) Y_pred=W[1 ]*x1_test+W[2 ]*x2_test+W[0 ] print ("预测价格:" ,round (Y_pred,2 ),"万元" )
结果如下:
The X is:
[[ 1. 137.97 3. ]
[ 1. 104.5 2. ]
[ 1. 100. 2. ]
[ 1. 124.32 3. ]
[ 1. 79.2 1. ]
[ 1. 99. 2. ]
[ 1. 124. 3. ]
[ 1. 114. 2. ]
[ 1. 106.69 2. ]
[ 1. 138.05 3. ]
[ 1. 53.75 1. ]
[ 1. 46.91 1. ]
[ 1. 68. 1. ]
[ 1. 63.02 1. ]
[ 1. 81.26 2. ]
[ 1. 86.21 2. ]]
The Y is:
[[145. ]
[110. ]
[ 93. ]
[116. ]
[ 65.32]
[104. ]
[118. ]
[ 91. ]
[ 62. ]
[133. ]
[ 51. ]
[ 45. ]
[ 78.5 ]
[ 69.65]
[ 75.69]
[ 95.3 ]]
The W is:
[[11.96729093]
[ 0.53488599]
[14.33150378]]
多元线性回归方程:Y=0.5348859949724512*x1+14.331503777673632*x2+11.967290930536517
请输入房屋面积和房间数,预测房屋销售价格:
商品房面积:140
房间数:3
预测价格: 129.85 万元
三维模型可视化 1 2 3 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
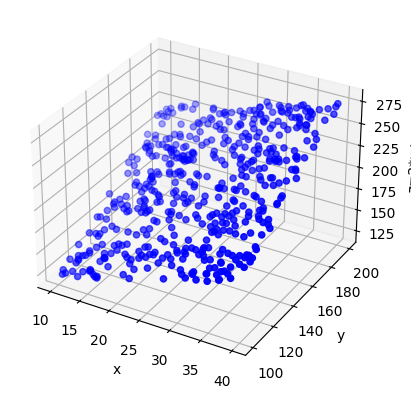
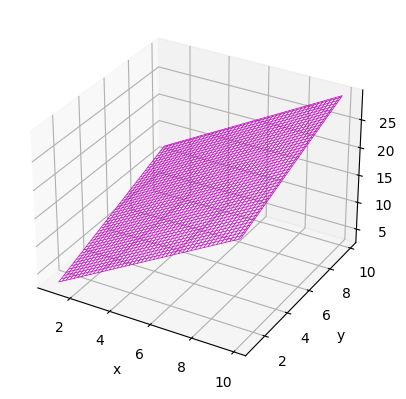
1.绘制散点图 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 fig=plt.figure(num="Scatter" ) ax1=plt.axes(projection='3d' ) x=np.random.uniform(10 ,40 ,500 ) y=np.random.uniform(100 ,200 ,500 ) z=2 *x+y ax1.scatter(x,y,z,c="b" ) ax1.set_xlabel("x" ) ax1.set_ylabel("y" ) ax1.set_zlabel("z=2*x+y" ) plt.show()
结果如下:
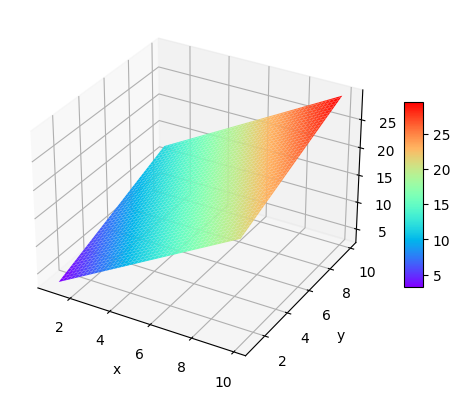
2.绘制平面图 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 x=np.arange(1 ,10 ,0.1 ) y=np.arange(1 ,10 ,0.1 ) X,Y=np.meshgrid(x,y) Z=2 *X+Y fig=plt.figure(num="Suface" ) ax2=plt.axes(projection='3d' ) surf=ax2.plot_surface(X,Y,Z,cmap="rainbow" ) ax2.set_xlabel("x" ) ax2.set_ylabel("y" ) ax2.set_zlabel("z=2*x+y" ) fig.colorbar(surf,shrink=0.5 ,aspect=10 ) plt.show()
结果如下:
3.绘制线框图 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 x=np.arange(1 ,10 ,0.1 ) y=np.arange(1 ,10 ,0.1 ) X,Y=np.meshgrid(x,y) Z=2 *X+Y fig=plt.figure(num="wireframe" ) ax3=plt.axes(projection='3d' ) ax3.plot_wireframe(X,Y,Z,color="m" ,linewidth=0.5 ) ax3.set_xlabel("x" ) ax3.set_ylabel("y" ) ax3.set_zlabel("z=2*x+y" ) plt.show()
结果如下:
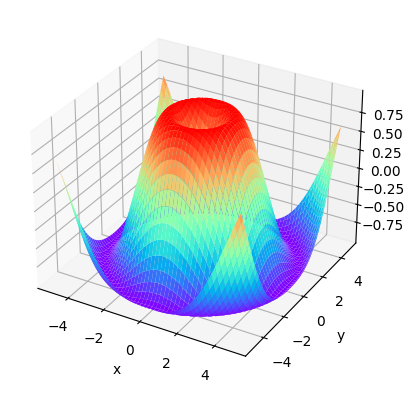
4.绘制曲面图 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 x=np.arange(-5 ,5 ,0.1 ) y=np.arange(-5 ,5 ,0.1 ) X,Y=np.meshgrid(x,y) Z=np.sin(np.sqrt(X**2 +Y**2 )) fig=plt.figure(num="曲面图" ) ax4=plt.axes(projection='3d' ) ax4.plot_surface(X,Y,Z,cmap="rainbow" ) ax4.set_xlabel("x" ) ax4.set_ylabel("y" ) plt.show()
结果如下:
梯度下降法实现线性回归 1.NumPy实现
一元线性回归
加载样本数据x、y
设置超参数学习率、迭代次数
设置模型参数初值w0、b0
训练模型w、b
结果可视化
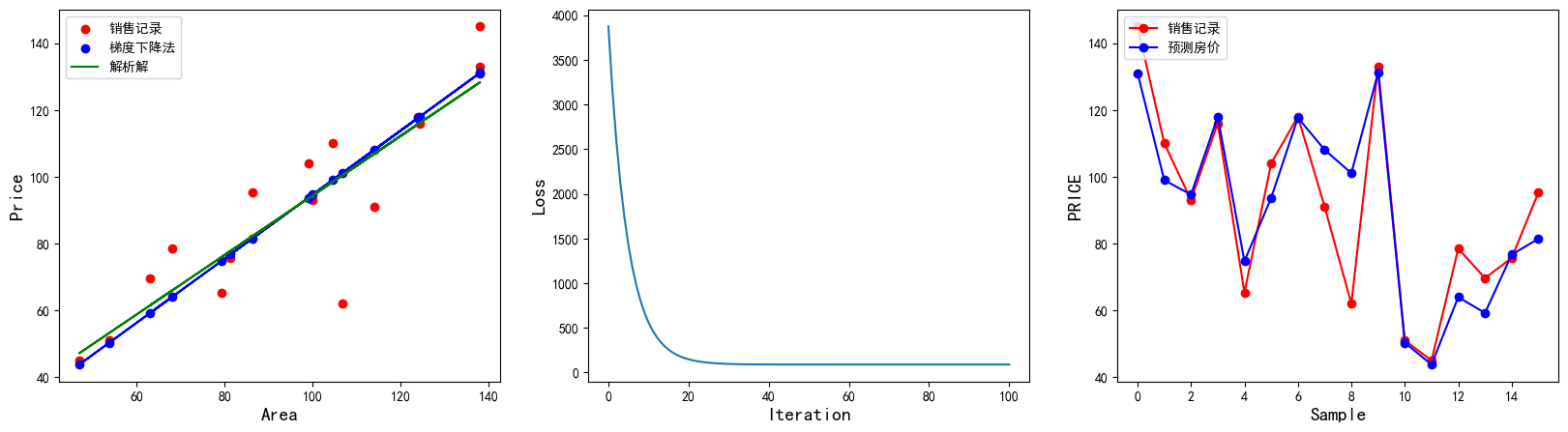
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt%matplotlib inline x=np.array([137.97 ,104.50 ,100.00 ,124.32 ,79.20 ,99.00 ,124.00 ,114.00 ,106.69 ,138.05 ,53.75 ,46.91 ,68.00 ,63.02 ,81.26 ,86.21 ]) y=np.array([145.00 ,110.00 ,93.00 ,116.00 ,65.32 ,104.00 ,118.00 ,91.00 ,62.00 ,133.00 ,51.00 ,45.00 ,78.50 ,69.65 ,75.69 ,95.30 ]) learn_rate=0.00001 iter =100 display_step=10 np.random.seed(612 ) w=np.random.randn() b=np.random.randn() mse=[] for i in range (0 ,iter +1 ): dL_dw=np.mean(x*(w*x+b-y)) dL_db=np.mean(w*x+b-y) w=w-learn_rate*dL_dw b=b-learn_rate*dL_db pred=w*x+b Loss=np.mean(np.square(y-pred))/2 mse.append(Loss) if i % display_step==0 : print ("i:%i, Loss:%f, w:%f, b:%f" %(i,mse[i],w,b)) plt.figure(figsize=(20 ,5 )) plt.rcParams["font.sans-serif" ]="SimHei" plt.rcParams["axes.unicode_minus" ]=False plt.subplot(1 ,3 ,1 ) plt.scatter(x,y,color="red" ,label="销售记录" ) plt.scatter(x,pred,color="blue" ,label="梯度下降法" ) plt.plot(x,pred,color="blue" ) plt.plot(x,0.89 *x+5.41 ,color="green" ,label="解析解" ) plt.xlabel("Area" ,fontsize=14 ) plt.ylabel("Price" ,fontsize=14 ) plt.legend(loc="upper left" ) plt.subplot(1 ,3 ,2 ) plt.plot(mse) plt.xlabel("Iteration" ,fontsize=14 ) plt.ylabel("Loss" ,fontsize=14 ) plt.subplot(1 ,3 ,3 ) plt.plot(y,color="red" ,marker="o" ,label="销售记录" ) plt.plot(pred,color="blue" ,marker="o" ,label="预测房价" ) plt.xlabel("Sample" ,fontsize=14 ) plt.ylabel("PRICE" ,fontsize=14 ) plt.legend(loc="upper left" ) plt.show()
结果如下:
i:0, Loss:3874.243711, w:0.082565, b:-1.161967
i:10, Loss:562.072704, w:0.648552, b:-1.156446
i:20, Loss:148.244254, w:0.848612, b:-1.154462
i:30, Loss:96.539782, w:0.919327, b:-1.153728
i:40, Loss:90.079712, w:0.944323, b:-1.153435
i:50, Loss:89.272557, w:0.953157, b:-1.153299
i:60, Loss:89.171687, w:0.956280, b:-1.153217
i:70, Loss:89.159061, w:0.957383, b:-1.153156
i:80, Loss:89.157460, w:0.957773, b:-1.153101
i:90, Loss:89.157238, w:0.957910, b:-1.153048
i:100, Loss:89.157187, w:0.957959, b:-1.152997
多元线性回归
加载数据样本
数据处理:归一化、堆叠
设置超参数:学习率、迭代次数
设置模型参数的初值Wo
训练模型W:
结果可视化
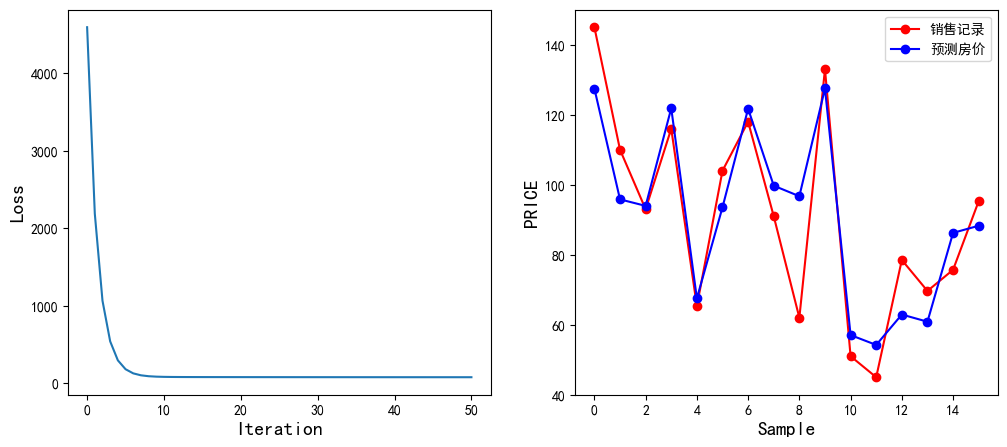
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 import tensorflow as tfimport numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltarea=np.array([137.97 ,104.50 ,100.00 ,124.32 ,79.20 ,99.00 ,124.00 ,114.00 ,106.69 ,138.05 ,53.75 ,46.91 ,68.00 ,63.02 ,81.26 ,86.21 ]) room=np.array([3 ,2 ,2 ,3 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,2 ,2 ,3 ,1 ,1 ,1 ,1 ,2 ,2 ]) price=np.array([145.00 ,110.00 ,93.00 ,116.00 ,65.32 ,104.00 ,118.00 ,91.00 ,62.00 ,133.00 ,51.00 ,45.00 ,78.50 ,69.65 ,75.69 ,95.30 ]) num=len (area) x0=np.ones(num) x1=(area-area.min ())/(area.max ()-area.min ()) x2=(room-room.min ())/(room.max ()-room.min ()) X=np.stack((x0,x1,x2),axis=1 ) Y=price.reshape(-1 ,1 ) learn_rate=0.2 iter =50 display_step=10 np.random.seed(612 ) W=np.random.randn(3 ,1 ) mse=[] for i in range (0 ,iter +1 ): PRED=np.matmul(X,W) Loss=np.mean(np.square(Y-PRED))/2 mse.append(Loss) dL_dW=np.matmul(np.transpose(X),np.matmul(X,W)-Y)/num W=W-learn_rate*dL_dW if i % display_step==0 : print ("i: %i, Loss:%f" % (i,mse[i])) plt.figure(figsize=(12 ,5 )) plt.rcParams["font.sans-serif" ]="SimHei" plt.rcParams["axes.unicode_minus" ]=False plt.subplot(1 ,2 ,1 ) plt.plot(mse) plt.xlabel("Iteration" ,fontsize=14 ) plt.ylabel("Loss" ,fontsize=14 ) plt.subplot(1 ,2 ,2 ) PRED=PRED.reshape(-1 ) plt.plot(price,color="red" ,marker="o" ,label="销售记录" ) plt.plot(PRED,color="blue" ,marker="o" ,label="预测房价" ) plt.xlabel("Sample" ,fontsize=14 ) plt.ylabel("PRICE" ,fontsize=14 ) plt.legend(loc="upper right" ) plt.show()
结果如下:
i: 0, Loss:4593.851656
i: 10, Loss:85.480869
i: 20, Loss:82.080953
i: 30, Loss:81.408948
i: 40, Loss:81.025841
i: 50, Loss:80.803450
2.TensorFlow实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 import tensorflow as tfimport numpy as npx=np.array([137.97 ,104.50 ,100.00 ,124.32 ,79.20 ,99.00 ,124.00 ,114.00 ,106.69 ,138.05 ,53.75 ,46.91 ,68.00 ,63.02 ,81.26 ,86.21 ]) y=np.array([145.00 ,110.00 ,93.00 ,116.00 ,65.32 ,104.00 ,118.00 ,91.00 ,62.00 ,133.00 ,51.00 ,45.00 ,78.50 ,69.65 ,75.69 ,95.30 ]) learn_rate=0.0001 iter =10 display_step=1 np.random.seed(612 ) w=tf.Variable(np.random.randn()) b=tf.Variable(np.random.randn()) mse=[] for i in range (0 ,iter +1 ): with tf.GradientTape() as tape: pred=w*x+b Loss=0.5 *tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y-pred)) mse.append(Loss) dL_dw,dL_db=tape.gradient(Loss,[w,b]) w.assign_sub(learn_rate*dL_dw) b.assign_sub(learn_rate*dL_db) if i % display_step==0 : print ("i: %i,Loss: %f, w: %f, b: %f" % (i,Loss,w.numpy(),b.numpy()))
结果如下:
i: 0,Loss: 4749.362305, w: 0.946047, b: -1.153577
i: 1,Loss: 89.861862, w: 0.957843, b: -1.153412
i: 2,Loss: 89.157501, w: 0.957987, b: -1.153359
i: 3,Loss: 89.157379, w: 0.957988, b: -1.153308
i: 4,Loss: 89.157364, w: 0.957988, b: -1.153257
i: 5,Loss: 89.157318, w: 0.957987, b: -1.153206
i: 6,Loss: 89.157280, w: 0.957987, b: -1.153155
i: 7,Loss: 89.157265, w: 0.957986, b: -1.153104
i: 8,Loss: 89.157219, w: 0.957986, b: -1.153052
i: 9,Loss: 89.157211, w: 0.957985, b: -1.153001
i: 10,Loss: 89.157196, w: 0.957985, b: -1.152950
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 import numpy as nparea=np.array([137.97 ,104.50 ,100.00 ,124.32 ,79.20 ,99.00 ,124.00 ,114.00 ,106.69 ,138.05 ,53.75 ,46.91 ,68.00 ,63.02 ,81.26 ,86.21 ]) room=np.array([3 ,2 ,2 ,3 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,2 ,2 ,3 ,1 ,1 ,1 ,1 ,2 ,2 ]) price=np.array([145.00 ,110.00 ,93.00 ,116.00 ,65.32 ,104.00 ,118.00 ,91.00 ,62.00 ,133.00 ,51.00 ,45.00 ,78.50 ,69.65 ,75.69 ,95.30 ]) num=len (area) x0=np.ones(num) x1=(area-area.min ())/(area.max ()-area.min ()) x2=(room-room.min ())/(room.max ()-room.min ()) X=np.stack((x0,x1,x2),axis=1 ) Y=price.reshape(-1 ,1 ) learn_rate=0.2 iter =50 display_step=10 np.random.seed(612 ) W=tf.Variable(np.random.randn(3 ,1 )) mse=[] for i in range (0 ,iter +1 ): with tf.GradientTape() as tape: PRED=tf.matmul(X,W) Loss=0.5 *tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(Y-PRED)) mse.append(Loss) dL_dW=tape.gradient(Loss,W) W.assign_sub(learn_rate*dL_dW) if i % display_step==0 : print ("i: %i, Loss: %f" % (i,Loss))
结果如下:
i: 0, Loss: 4593.851656
i: 10, Loss: 85.480869
i: 20, Loss: 82.080953
i: 30, Loss: 81.408948
i: 40, Loss: 81.025841
i: 50, Loss: 80.803450
TensorFlow的可训练变量和自动求导机制 1.Variable对象
tf.Variable(initial_value,dtype)#initial_value可以是数字、Python列表、ndarray对象、Tensor对象可训练变量赋值:
对象名.assign()
对象名.assign_add()
对象名.assign_sub()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 x=tf.Variable([[1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ],[4 ,5 ,6 ,7 ]]) print (x)print (x.trainable)print (x.assign([[1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ],[4 ,5 ,6 ,7 ]]))print (x.assign_add([[3 ,2 ,4 ,5 ],[3 ,7 ,8 ,1 ]]))print (x.assign_sub([[3 ,2 ,4 ,5 ],[3 ,7 ,8 ,1 ]]))
结果如下:
<tf.Variable 'Variable:0' shape=(2, 4) dtype=int32, numpy=
array([[1, 2, 3, 4],
[4, 5, 6, 7]])>
True
<tf.Variable 'UnreadVariable' shape=(2, 4) dtype=int32, numpy=
array([[1, 2, 3, 4],
[4, 5, 6, 7]])>
<tf.Variable 'UnreadVariable' shape=(2, 4) dtype=int32, numpy=
array([[ 4, 4, 7, 9],
[ 7, 12, 14, 8]])>
<tf.Variable 'UnreadVariable' shape=(2, 4) dtype=int32, numpy=
array([[1, 2, 3, 4],
[4, 5, 6, 7]])>
2.自动求导机制
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 x=tf.Variable(3.0 ) with tf.GradientTape() as tape: y=tf.square(x) dy_dx=tape.gradient(y,x) print (y)print (dy_dx)
结果如下:
tf.Tensor([9.], shape=(1,), dtype=float32)
tf.Tensor([6.], shape=(1,), dtype=float32)
GradientTape()的persistent参数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 x=tf.Variable(3.0 ) with tf.GradientTape(persistent=True ) as tape: y=tf.square(x) z=tf.pow (x,3 ) dy_dx=tape.gradient(y,x) dz_dx=tape.gradient(z,x) print (y)print (dy_dx)print (40 *"-" )print (z)print (dz_dx)del tape
结果如下:
tf.Tensor(9.0, shape=(), dtype=float32)
tf.Tensor(6.0, shape=(), dtype=float32)
----------------------------------------
tf.Tensor(27.0, shape=(), dtype=float32)
tf.Tensor(27.0, shape=(), dtype=float32)
GradientTape()的watch_accessed_variables参数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 x=tf.Variable(3.0 ) with tf.GradientTape(watch_accessed_variables=False ) as tape: tape.watch(x) y=tf.square(x) dy_dx=tape.gradient(y,x) print (y)print (dy_dx)
结果如下:
tf.Tensor(9.0, shape=(), dtype=float32)
tf.Tensor(6.0, shape=(), dtype=float32)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 x=tf.constant(3.0 ) with tf.GradientTape(watch_accessed_variables=False ) as tape: tape.watch(x) y=tf.square(x) dy_dx=tape.gradient(y,x) print (y)print (dy_dx)
结果如下:
tf.Tensor(9.0, shape=(), dtype=float32)
tf.Tensor(6.0, shape=(), dtype=float32)
多元函数求偏导tape.gradient(函数,自变量)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 x=tf.Variable(3.0 ) y=tf.Variable(4.0 ) with tf.GradientTape() as tape: f=tf.square(x)+2 *tf.square(y)+1 df_dx,df_dy=tape.gradient(f,[x,y]) print (f)print (df_dx)print (df_dy)
结果如下:
tf.Tensor(42.0, shape=(), dtype=float32)
tf.Tensor(6.0, shape=(), dtype=float32)
tf.Tensor(16.0, shape=(), dtype=float32)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 x=tf.Variable(3.0 ) y=tf.Variable(4.0 ) with tf.GradientTape() as tape2: with tf.GradientTape() as tape1: f=tf.square(x)+2 *tf.square(y)+1 first_grads=tape1.gradient(f,[x,y]) second_grads=tape2.gradient(first_grads,[x,y]) print (f)print (first_grads)print (second_grads)
结果如下:
tf.Tensor(42.0, shape=(), dtype=float32)
[<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=6.0>, <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=16.0>]
[<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=2.0>, <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=4.0>]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 x=tf.Variable([1.0 ,2.0 ,3.0 ]) y=tf.Variable([4.0 ,5.0 ,6.0 ]) with tf.GradientTape() as tape: f=tf.square(x)+2 *tf.square(y)+1 df_dx,df_dy=tape.gradient(f,[x,y]) print (f)print (df_dx)print (df_dy)
结果如下:
tf.Tensor([34. 55. 82.], shape=(3,), dtype=float32)
tf.Tensor([2. 4. 6.], shape=(3,), dtype=float32)
tf.Tensor([16. 20. 24.], shape=(3,), dtype=float32)
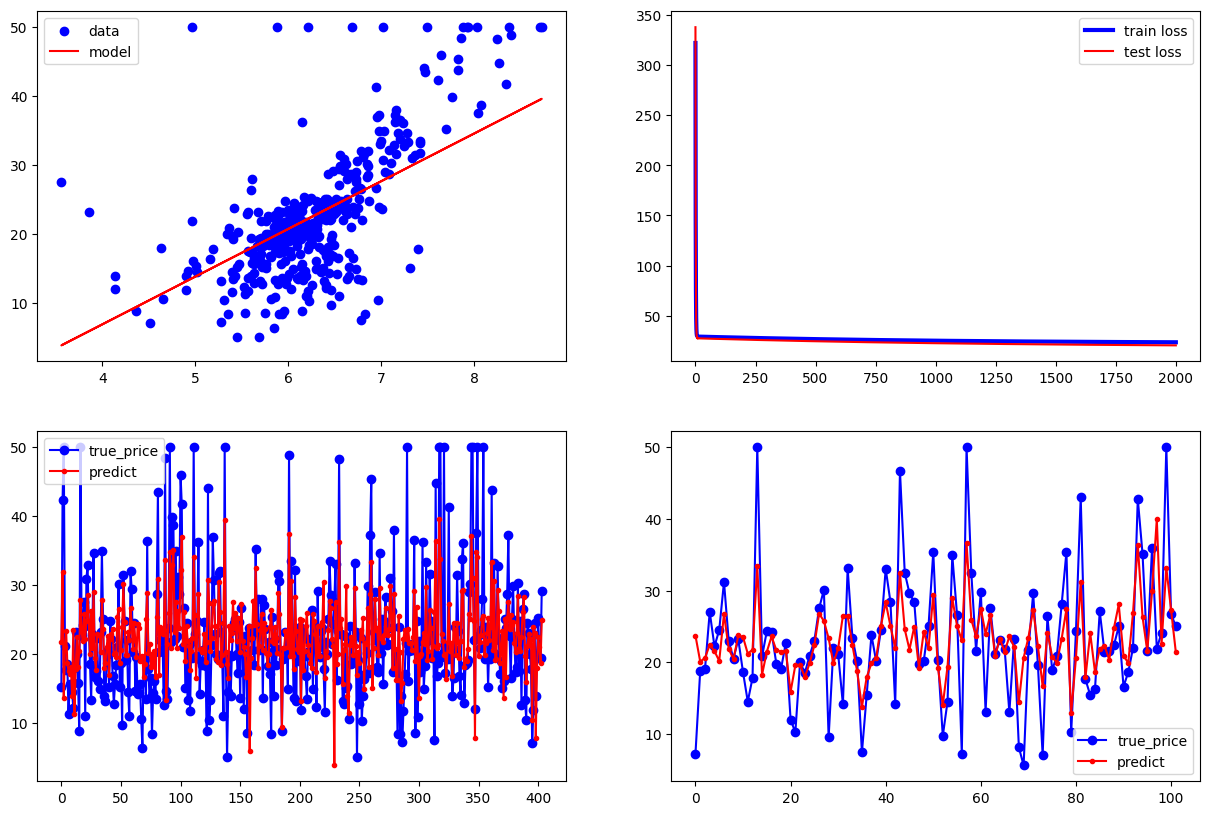
实例分析:波士顿房价预测 1.平均房间数与房价的关系 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 import tensorflow as tfimport numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltboston_housing = tf.keras.datasets.boston_housing (train_x,train_y),(test_x,test_y)=boston_housing.load_data() x_train=train_x[:,5 ] y_train=train_y x_test=test_x[:,5 ] y_test=test_y learn_rate=0.04 iter =2000 display_step=200 np.random.seed(612 ) w=tf.Variable(np.random.randn()) b=tf.Variable(np.random.randn()) mse_train=[] mse_test=[] for i in range (0 ,iter +1 ): with tf.GradientTape() as tape: pred_train=w*x_train+b loss_train=0.5 *tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_train-pred_train)) pred_test=w*x_test+b loss_test=0.5 *tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_test-pred_test)) mse_train.append(loss_train) mse_test.append(loss_test) dL_dw,dL_db=tape.gradient(loss_train,[w,b]) w.assign_sub(learn_rate*dL_dw) b.assign_sub(learn_rate*dL_db) if i % display_step==0 : print ("i:%i,\tTrain Loss:%f,\tTest Loss:%f" % (i,loss_train,loss_test)) plt.figure(figsize=(15 ,10 )) plt.subplot(221 ) plt.scatter(x_train,y_train,color="blue" ,label="data" ) plt.plot(x_train,pred_train,color="red" ,label="model" ) plt.legend(loc="upper left" ) plt.subplot(222 ) plt.plot(mse_train,color="blue" ,linewidth=3 ,label="train loss" ) plt.plot(mse_test,color="red" ,linewidth=1.5 ,label="test loss" ) plt.legend(loc="upper right" ) plt.subplot(223 ) plt.plot(y_train,color="blue" ,marker="o" ,label="true_price" ) plt.plot(pred_train,color="red" ,marker="." ,label="predict" ) plt.legend() plt.subplot(224 ) plt.plot(y_test,color="blue" ,marker="o" ,label="true_price" ) plt.plot(pred_test,color="red" ,marker="." ,label="predict" ) plt.legend() plt.show()
结果如下:
i:0, Train Loss:321.837585, Test Loss:337.568634
i:200, Train Loss:28.122616, Test Loss:26.237764
i:400, Train Loss:27.144739, Test Loss:25.099327
i:600, Train Loss:26.341949, Test Loss:24.141077
i:800, Train Loss:25.682899, Test Loss:23.332979
i:1000, Train Loss:25.141848, Test Loss:22.650162
i:1200, Train Loss:24.697670, Test Loss:22.072006
i:1400, Train Loss:24.333027, Test Loss:21.581432
i:1600, Train Loss:24.033667, Test Loss:21.164261
i:1800, Train Loss:23.787903, Test Loss:20.808695
i:2000, Train Loss:23.586145, Test Loss:20.504938
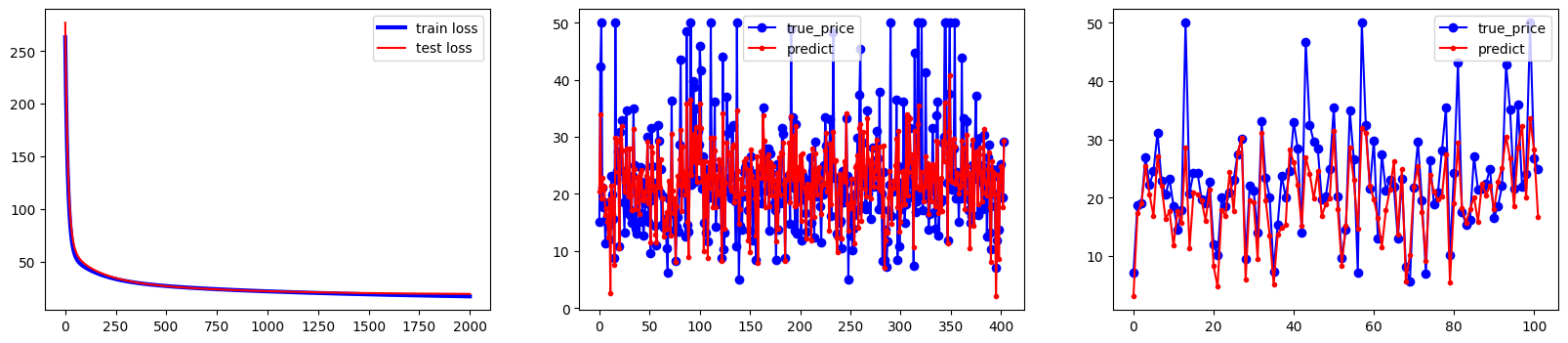
2.所有属性的多元线性回归 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 boston_housing = tf.keras.datasets.boston_housing (train_x,train_y),(test_x,test_y)=boston_housing.load_data() num_train=len (train_x) num_test=len (test_x) x_train=(train_x-train_x.min (axis=0 ))/(train_x.max (axis=0 )-train_x.min (axis=0 )) y_train=train_y x_test=(test_x-test_x.min (axis=0 ))/(test_x.max (axis=0 )-test_x.min (axis=0 )) y_test=test_y x0_train=np.ones(num_train).reshape(-1 ,1 ) x0_test=np.ones(num_test).reshape(-1 ,1 ) X_train=tf.concat([x0_train,x_train],axis=1 ) X_test=tf.concat([x0_test,x_test],axis=1 ) Y_train=tf.constant(y_train.reshape(-1 ,1 )) Y_test=tf.constant(y_test.reshape(-1 ,1 )) learn_rate=0.01 iter =2000 display_step=200 np.random.seed(612 ) W=tf.Variable(np.random.randn(14 ,1 )) mse_train=[] mse_test=[] for i in range (0 ,iter +1 ): with tf.GradientTape() as tape: PRED_train=tf.matmul(X_train,W) Loss_train=0.5 *tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(Y_train-PRED_train)) PRED_test=tf.matmul(X_test,W) Loss_test=0.5 *tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(Y_test-PRED_test)) mse_train.append(Loss_train) mse_test.append(Loss_test) dL_dW=tape.gradient(Loss_train,W) W.assign_sub(learn_rate*dL_dW) if i % display_step==0 : print ("i:%i,\tTrain Loss:%f,\tTest Loss:%f" % (i,Loss_train,Loss_test)) plt.figure(figsize=(20 ,4 )) plt.subplot(131 ) plt.plot(mse_train,color="blue" ,linewidth=3 ,label="train loss" ) plt.plot(mse_test,color="red" ,linewidth=1.5 ,label="test loss" ) plt.legend(loc="upper right" ) plt.subplot(132 ) plt.plot(Y_train,color="blue" ,marker="o" ,label="true_price" ) plt.plot(PRED_train,color="red" ,marker="." ,label="predict" ) plt.legend() plt.subplot(133 ) plt.plot(Y_test,color="blue" ,marker="o" ,label="true_price" ) plt.plot(PRED_test,color="red" ,marker="." ,label="predict" ) plt.legend() plt.show()
结果如下:
i:0, Train Loss:263.193459, Test Loss:276.994119
i:200, Train Loss:36.176548, Test Loss:37.562946
i:400, Train Loss:28.789464, Test Loss:28.952521
i:600, Train Loss:25.520702, Test Loss:25.333921
i:800, Train Loss:23.460534, Test Loss:23.340539
i:1000, Train Loss:21.887280, Test Loss:22.039745
i:1200, Train Loss:20.596287, Test Loss:21.124848
i:1400, Train Loss:19.510205, Test Loss:20.467240
i:1600, Train Loss:18.587010, Test Loss:19.997707
i:1800, Train Loss:17.797461, Test Loss:19.671583
i:2000, Train Loss:17.118926, Test Loss:19.456854